The emerging roles of Gα12/13 proteins on the hallmarks of cancer in solid tumors
- PMID: 34689178
- PMCID: PMC8732267
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-021-02069-w
The emerging roles of Gα12/13 proteins on the hallmarks of cancer in solid tumors
Abstract
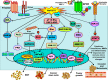
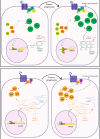
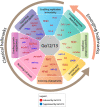
G12 proteins comprise a subfamily of G-alpha subunits of heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins (G proteins) that link specific cell surface G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) to downstream signaling molecules and play important roles in human physiology. The G12 subfamily contains two family members: Gα12 and Gα13 (encoded by the GNA12 and GNA13 genes, respectively) and, as with all G proteins, their activity is regulated by their ability to bind to guanine nucleotides. Increased expression of both Gα12 and Gα13, and their enhanced signaling, has been associated with tumorigenesis and tumor progression of multiple cancer types over the past decade. Despite these strong associations, Gα12/13 proteins are underappreciated in the field of cancer. As our understanding of G protein involvement in oncogenic signaling has evolved, it has become clear that Gα12/13 signaling is pleotropic and activates specific downstream effectors in different tumor types. Further, the expression of Gα12/13 proteins is regulated through a series of transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms, several of which are frequently deregulated in cancer. With the ever-increasing understanding of tumorigenic processes driven by Gα12/13 proteins, it is becoming clear that targeting Gα12/13 signaling in a context-specific manner could provide a new strategy to improve therapeutic outcomes in a number of solid tumors. In this review, we detail how Gα12/13 proteins, which were first discovered as proto-oncogenes, are now known to drive several "classical" hallmarks, and also play important roles in the "emerging" hallmarks, of cancer.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GNA13 suppresses proliferation of ER+ breast cancer cells via ERα dependent upregulation of the MYC oncogene.Breast Cancer Res. 2024 Jul 4;26(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01866-x. Breast Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38965558 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent C-terminal motifs in Gα12 and Gα13 provide distinct mechanisms of effector binding and SRF activation.Cell Signal. 2020 Aug;72:109653. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109653. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 32330601
-
Heterotrimeric Gα12/13 proteins in kidney injury and disease.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 Mar 1;318(3):F660-F672. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00453.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31984793 Review.
-
GEP oncogene promotes cell proliferation through YAP activation in ovarian cancer.Oncogene. 2016 Aug 25;35(34):4471-80. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.505. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26804165
-
GPCR-Gα13 Involvement in Mitochondrial Function, Oxidative Stress, and Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 28;25(13):7162. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137162. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000269 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chemokines and cytokines: Axis and allies in prostate cancer pathogenesis.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Nov;86(Pt 3):497-512. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.02.017. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 35181473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiRNA-132/212 encapsulated by adipose tissue-derived exosomes worsen atherosclerosis progression.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Sep 9;23(1):331. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02404-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39252021 Free PMC article.
-
Gα12 and Gα13: Versatility in Physiology and Pathology.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 14;10:809425. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.809425. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35237598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BRAFΔβ3-αC in-frame deletion mutants differ in their dimerization propensity, HSP90 dependence, and druggability.Sci Adv. 2023 Sep;9(35):eade7486. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ade7486. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37656784 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis Expands lncRNA Functional Profiles in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 2;25(15):8456. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158456. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39126025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rohrer DK, Kobilka BK. G protein-coupled receptors: functional and mechanistic insights through altered gene expression. Physiol Rev. 1998;78:35–52. - PubMed
-
- Lappano R, Maggiolini M. G protein-coupled receptors: novel targets for drug discovery in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10:47–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

