Structural characterization of the thermal unfolding pathway of human VEGFR1 D2 domain
- PMID: 34689403
- PMCID: PMC9299094
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.16246
Structural characterization of the thermal unfolding pathway of human VEGFR1 D2 domain
Abstract
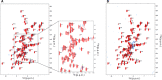
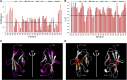
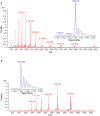
Folding stability is a crucial feature of protein evolution and is essential for protein functions. Thus, the comprehension of protein folding mechanisms represents an important complement to protein structure and function, crucial to determine the structural basis of protein misfolding. In this context, thermal unfolding studies represent a useful tool to get a molecular description of the conformational transitions governing the folding/unfolding equilibrium of a given protein. Here, we report the thermal folding/unfolding pathway of VEGFR1D2, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily by means of a high-resolution thermodynamic approach that combines differential scanning calorimetry with atomic-level unfolding monitored by NMR. We show how VEGFR1D2 folding is driven by an oxidatively induced disulfide pairing: the key event in the achievement of its functional structure is the formation of a small hydrophobic core that surrounds a disulfide bridge. Such a 'folding nucleus' induces the cooperative transition to the properly folded conformation supporting the hypothesis that a disulfide bond can act as a folding nucleus that eases the folding process.
Keywords: DSC; NMR; VEGF; disulfide bond; thermal unfolding.
© 2021 The Authors. The FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ferrara N & Davis‐Smyth T (1997) The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr Rev 18, 4–25. - PubMed
-
- Klagsbrun M & D’Amore PA (1996) Vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 7, 259–270. - PubMed
-
- Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J & Claesson‐Welsh L (2006) VEGF receptor signalling – in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7, 359–371. - PubMed
-
- van der Geer P, Hunter T & Lindberg RA (1994) Receptor protein‐tyrosine kinases and their signal transduction pathways. Annu Rev Cell Biol 10, 251–337. - PubMed
-
- de Vries C, Escobedo JA, Ueno H, Houck K, Ferrara N & Williams LT (1992) The fms‐like tyrosine kinase, a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Science 255, 989–991. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

