Sirtuin 1 in Endothelial Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Aging
- PMID: 34690807
- PMCID: PMC8527036
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.733696
Sirtuin 1 in Endothelial Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Aging
Abstract
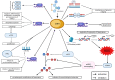
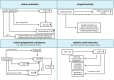
Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) is a histone deacetylase belonging to the family of Sirtuins, a class of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent enzymes with multiple metabolic functions. SIRT1 localizes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, and is implicated in the regulation of cell survival in response to several stimuli, including metabolic ones. The expression of SIRT1 is associated with lifespan and is reduced with aging both in animal models and in humans, where the lack of SIRT1 is regarded as a potential mediator of age-related cardiovascular diseases. In this review, we will summarize the extensive evidence linking SIRT1 functional and quantitative defects to cellular senescence and aging, with particular regard to their role in determining endothelial dysfunction and consequent cardiovascular diseases. Ultimately, we outline the translational perspectives for this topic, in order to highlight the missing evidence and the future research steps.
Keywords: aging–old age–seniors; atherosclerosis; cardiovascular disease; eNOS (endothelial nitric oxide synthase); endothelial (dys)function; inflammaging; sirtuin (SIRT1).
Copyright © 2021 Ministrini, Puspitasari, Beer, Liberale, Montecucco and Camici.
Conflict of interest statement
GC is coinventor on the International Patent WO/2020/226993 filed in April 2020. The patent relates to the use of antibodies which specifically bind IL-1α to reduce various sequelae of ischemia-reperfusion injury to the central nervous system. GC is a consultant to Sovida solutions limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

