Pathogenic Mechanism of Der p 38 as a Novel Allergen Homologous to RipA and RipB Proteins in Atopic Dermatitis
- PMID: 34691014
- PMCID: PMC8531521
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.646316
Pathogenic Mechanism of Der p 38 as a Novel Allergen Homologous to RipA and RipB Proteins in Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
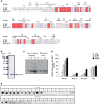
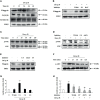
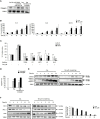
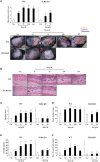
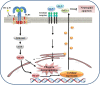
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic relapsing pruritic disease encompassing skin inflammation and barrier dysfunction. House dust mites are key allergens that augment the development of atopic dermatitis. We aimed to investigate the pathogenic mechanism of AD due to Der p 38, recently identified by us. The frequency of IgE reactivity to Der p 38 in AD subjects was 52.6% (10/19) in the skin prick test and 57.9% (11/19) in the dot blot assay. In human keratinocyte HaCaT cells, Der p 38 triggered the impairment of filaggrin expression and induced pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-8 and MCP-1 through TLR4, PI3K, AKT, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and NF-κB pathway. Supernatants from Der p 38-treated cells blocked filaggrin expression and neutrophil apoptosis. The anti-apoptotic effect of the Der p 38-released molecules on neutrophils was accomplished by inhibition of the caspase 9/3 pathway, and by increased MCL-1 expression and BCL-2/BAX expression ratio. In C57BL/6 wild type (WT) mice, Der p 38 induced a dose-dependent increase of AD-like skin lesions, with enhanced expressions of total and Der p 38-specific IgE. Der p 38 also diminished the expressions of skin barrier proteins and induced JNK activation. However, the AD-like features following cutaneous Der p 38 exposure were observed to be reduced in the TLR4 knockout (KO) group, as compared to the WT group. Skin infiltration of neutrophils, eosinophils and mast cells was increased in the WT mice, but was not portrayed in the TLR4 KO mice. These findings indicate that Der p 38 is a novel mite allergen that triggers AD by lowering skin barrier proteins and increasing inflammatory cells. Results of this study have thereby paved the way to unveil the pathogenic mechanisms of AD.
Keywords: Der p 38; TLR4; atopic dermatitis; filaggrin; skin barrier.
Copyright © 2021 Jeon, Kim, Kashif, Hong, Lee, Hong, Park, Yang and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Der f 38 Is a Novel TLR4-Binding Allergen Related to Allergy Pathogenesis from Dermatophagoides farinae.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 5;22(16):8440. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168440. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445142 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of sublingual immunotherapy with Dermatophagoides farinae vaccine in a murine atopic dermatitis model.Clin Exp Allergy. 2015 Apr;45(4):815-22. doi: 10.1111/cea.12417. Clin Exp Allergy. 2015. PMID: 25258013
-
Alpinia officinarum water extract inhibits the atopic dermatitis-like responses in NC/Nga mice by regulation of inflammatory chemokine production.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Dec;144:112322. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112322. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34656059
-
Dissecting the causes of atopic dermatitis in children: less foods, more mites.Allergol Int. 2012 Jun;61(2):231-43. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.11-RA-0371. Epub 2012 Feb 25. Allergol Int. 2012. PMID: 22361514 Review.
-
Allergy and the skin.Clin Exp Immunol. 2008 Sep;153 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):27-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03718.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18721326 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New approaches to immunotherapy in house dust mite allergy.Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023 Apr;66(4):161-168. doi: 10.3345/cep.2022.00479. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36397261 Free PMC article.
-
The novel house dust mite allergen Der p 39 exacerbates atopic dermatitis-like inflammation in mice by inducing skin barrier dysfunction.World Allergy Organ J. 2025 Mar 13;18(3):101036. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2025.101036. eCollection 2025 Mar. World Allergy Organ J. 2025. PMID: 40196722 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoproteasome Inhibition Reduces the T Helper 2 Response in Mouse Models of Allergic Airway Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2022 May 30;13:870720. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.870720. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35711460 Free PMC article.
-
An Atopic Dermatitis-Like Mouse Model by Alternate Epicutaneous Application of Dinitrofluorobenzene and an Extract of Dermatophagoides Farinae.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 15;9:843230. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.843230. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35783608 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

