Plasma EVs Display Antigen-Presenting Characteristics in Patients With Allergic Rhinitis and Promote Differentiation of Th2 Cells
- PMID: 34691024
- PMCID: PMC8531542
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.710372
Plasma EVs Display Antigen-Presenting Characteristics in Patients With Allergic Rhinitis and Promote Differentiation of Th2 Cells
Abstract
Background: Allergic rhinitis (AR) is characterized by IgE-mediated mucosa response after exposure to allergens. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nano-size vesicles containing biological cargos for intercellular communications. However, the role of plasma EVs in pathogenesis of AR remains largely unknown.
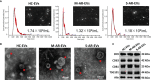
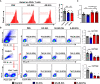
Methods: Plasma EVs from patients with AR were isolated, quantified, and characterized. The expression of Der p 1 and antigen-presenting molecules on EVs was determined by Western blot, flow cytometry, or ELISA. PKH26- and CFSE (carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester)-stained AR-EVs were used to determine the uptake of EVs by CD4+T cells and their effects on CD4+T cell proliferation, respectively.
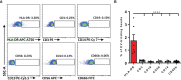
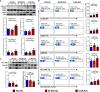
Results: Plasma EVs in healthy control (HC) and AR patients were similar in the concentration of particles, expression for specific EV markers, and both had structural lipid bilayer. However, the levels of Der p 1 on plasma EVs from both mild and moderate-severe AR patients were significantly higher than that on HC. The levels of antigen-presenting molecules on plasma EVs were similar from three subjects. Moreover, levels of Der p 1 on EVs in plasma, but not nasal secretion, were significantly associated with the symptom score of AR patients and level of plasma IL-13. Additionally, plasma EVs from patients with AR promoted the development of Th2 cells, while no effect was found on CD4+ T-cell proliferation.
Conclusions: Plasma EVs derived from patients with AR exhibited antigen-presenting characteristics and promoted differentiation of Th2 cells, thus providing novel understanding of the pathogenesis of AR.
Keywords: Der p 1; allergic rhinitis; antigen presentation; extracellular vesicles; type 2 T helper cells.
Copyright © 2021 Fang, Zhou, Peng, Liu, He, Chen, Chen and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 Update (in Collaboration With the World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy (2008) 63(Suppl 86):8–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2007.01620.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

