Auricular Acupressure Therapy for Patients with Cancer with Sleep Disturbance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34691214
- PMCID: PMC8531779
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/3996101
Auricular Acupressure Therapy for Patients with Cancer with Sleep Disturbance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Aim: We aim to provide available synthesized evidence of the efficacy and safety of auricular acupressure for cancer patients with sleep disturbance.
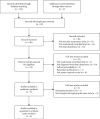
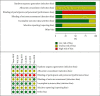
Methods: Randomized controlled clinical trials (RCTs) were identified from PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, The Cochrane Library, PsycINFO, Chinese Biomedical Database, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Chongqing VIP, and Wanfang Data, and the search date ranged from the inception of the databases to May 2021. Literature screening and data extraction were independently performed by three researchers. The Cochrane collaboration's tool for assessing the risk of bias was applied to evaluate the risk of bias of the RCTs included. The extracted data were analyzed using Rev-Man 5.4.1 software.
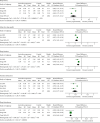
Results: Nine trials involving 688 participants met the inclusion criteria and were included in the qualitative analysis; 6 trials involving 485 participants were included in the meta-analysis. Synthesized results showed that auricular acupressure had a significant effect on reducing the total Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) score (MD = -3.88, 95% CI (-5.24, -2.53), P < 0.00001), and the scores of five PSQI components, sleep latency (MD = -0.53, 95% CI (-0.73, -0.32), P < 0.00001), subjective sleep quality (MD = -0.79, 95% CI (-1.05, -0.53), P < 0.00001), sleep duration (MD = -0.50, 95% CI (-0.69, -0.31), P < 0.0001), daytime dysfunction (MD = -0.53, 95% CI (-0.77, -0.29), P < 0.0001), and sleep disturbances (MD = -0.54, 95% CI (-0.60, -0.49), P < 0.00001), were also obviously decreased after the intervention of auricular acupressure. Shenmen and heart were the most commonly selected auricular acupoints, the main intervention durations ranged from 10 to 42 days, and the pressing times of auricular acupoints were 1-6 times a day, 1-5 min each time. One trial reported slight and transient pain caused by auricular acupressure, while the remaining 8 trials did not report obvious side effects.
Conclusion: Auricular acupressure can significantly improve the sleep quality of cancer patients with sleep disturbance, with no obvious side effects. Rigorously designed clinical trials are necessary for the further support of the clinical application.
Copyright © 2021 Yunxia Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gonzalez B. D., Grandner M. A., Caminiti C. B., Hui S.-k. A. Cancer survivors in the workplace: sleep disturbance mediates the impact of cancer on healthcare expenditures and work absenteeism. Supportive Care in Cancer . 2018;26(12):4049–4055. doi: 10.1007/s00520-018-4272-4. [published Online First: 2018/06/06] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous