Intracavitary Electrocardiogram Guidance Aids Excavation of Rhythm Abnormalities in Patients with Occult Heart Disease
- PMID: 34691372
- PMCID: PMC8536431
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/2230383
Intracavitary Electrocardiogram Guidance Aids Excavation of Rhythm Abnormalities in Patients with Occult Heart Disease
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Intracavitary Electrocardiogram Guidance Aids Excavation of Rhythm Abnormalities in Patients with Occult Heart Disease.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9836495. doi: 10.1155/2023/9836495. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 38094787 Free PMC article.
Abstract
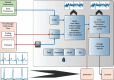
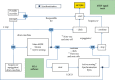
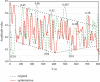
In this paper, the analysis of intracavitary electrocardiograms is used to guide the mining of abnormal cardiac rhythms in patients with hidden heart disease, and the algorithm is improved to address the data imbalance problem existing in the abnormal electrocardiogram signals, and a weight-based automatic classification algorithm for deep convolutional neural network electrocardiogram signals is proposed. By preprocessing the electrocardiogram data from the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database, the experimental dataset training algorithm model is obtained, and the algorithm model is migrated into the project. In terms of system design and implementation, by comparing the advantages and disadvantages of the electrocardiogram monitoring system platform, the overall design of the system was carried out in terms of functional and performance requirements according to the system realization goal, and a mobile platform system capable of classifying common abnormal electrocardiogram signals was developed. The system is capable of long-term monitoring and can invoke the automatic classification algorithm model of electrocardiogram signals for analysis. In this paper, the functional logic test and performance test were conducted on the main functional modules of the system. The test results show that the system can run stably and monitor electrocardiogram signals for a long time and can correctly call the deep convolutional neural network-based automatic electrocardiogram signal classification algorithm to analyze the electrocardiogram signals and achieve the requirements of displaying the electrocardiogram signal waveform, analyzing the heartbeat type, and calculating the average heart rate, which achieves the goal of real-time continuous monitoring and analysis of the electrocardiogram signals.
Copyright © 2021 Yanli Wei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Electrocardiogram Classification Based on Faster Regions with Convolutional Neural Network.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Jun 5;19(11):2558. doi: 10.3390/s19112558. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31195603 Free PMC article.
-
Electrocardiogram heartbeat classification based on a deep convolutional neural network and focal loss.Comput Biol Med. 2020 Aug;123:103866. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103866. Epub 2020 Jul 5. Comput Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32658786
-
ECG Heartbeat Classification Based on an Improved ResNet-18 Model.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Apr 30;2021:6649970. doi: 10.1155/2021/6649970. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. PMID: 34007306 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-Specific Heartbeat Classification in Single-Lead ECG using Convolutional Neural Network.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2021 Nov;2021:932-936. doi: 10.1109/EMBC46164.2021.9630366. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2021. PMID: 34891443
-
Arrhythmia Classification with ECG signals based on the Optimization-Enabled Deep Convolutional Neural Network.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020 Nov;196:105607. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105607. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020. PMID: 32593973
Cited by
-
Retracted: Intracavitary Electrocardiogram Guidance Aids Excavation of Rhythm Abnormalities in Patients with Occult Heart Disease.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9836495. doi: 10.1155/2023/9836495. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 38094787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- No-diabetes C. D. Asymptomatic patients without known heart disease have markers of occult heart disease left ventricular dysfunction is a sig. The American Journal of Cardiology . 2020;125(1449):1449–1453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

