Two-dimensional ferromagnetic superlattices
- PMID: 34692093
- PMCID: PMC8289050
- DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwz205
Two-dimensional ferromagnetic superlattices
Abstract
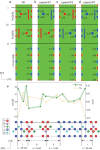
Mechanically exfoliated two-dimensional ferromagnetic materials (2D FMs) possess long-range ferromagnetic order and topologically nontrivial skyrmions in few layers. However, because of the dimensionality effect, such few-layer systems usually exhibit much lower Curie temperature (T C) compared to their bulk counterparts. It is therefore of great interest to explore effective approaches to enhance their T C, particularly in wafer-scale for practical applications. Here, we report an interfacial proximity-induced high-T C 2D FM Fe3GeTe2 (FGT) via A-type antiferromagnetic material CrSb (CS) which strongly couples to FGT. A superlattice structure of (FGT/CS)n, where n stands for the period of FGT/CS heterostructure, has been successfully produced with sharp interfaces by molecular-beam epitaxy on 2-inch wafers. By performing elemental specific X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) measurements, we have unequivocally discovered that T C of 4-layer Fe3GeTe2 can be significantly enhanced from 140 K to 230 K because of the interfacial ferromagnetic coupling. Meanwhile, an inverse proximity effect occurs in the FGT/CS interface, driving the interfacial antiferromagnetic CrSb into a ferrimagnetic state as evidenced by double-switching behavior in hysteresis loops and the XMCD spectra. Density functional theory calculations show that the Fe-Te/Cr-Sb interface is strongly FM coupled and doping of the spin-polarized electrons by the interfacial Cr layer gives rise to the T C enhancement of the Fe3GeTe2 films, in accordance with our XMCD measurements. Strikingly, by introducing rich Fe in a 4-layer FGT/CS superlattice, T C can be further enhanced to near room temperature. Our results provide a feasible approach for enhancing the magnetic order of few-layer 2D FMs in wafer-scale and render opportunities for realizing realistic ultra-thin spintronic devices.
Keywords: (Fe3GeTe2/CrSb)n superlattice; 2-inch Fe3GeTe2 film wafers; 2D ferromagnetic material; proximity effect; room temperature.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.
Figures
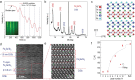
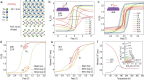
 . (e) Major and minor M-H loops at 2.5 K. (f) ZFC-FC data under 200 Oe for (FGT/CS)3 superlattice. TC is roughly determined to be ∼201 K, comparable to 206.3 ± 1.6 K as deduced by the Arrott-plots in the inset.
. (e) Major and minor M-H loops at 2.5 K. (f) ZFC-FC data under 200 Oe for (FGT/CS)3 superlattice. TC is roughly determined to be ∼201 K, comparable to 206.3 ± 1.6 K as deduced by the Arrott-plots in the inset.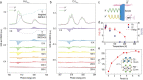

References
-
- Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SVet al. . Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nature 2005; 438: 197–200. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Tan Y-W, Stormer HLet al. . Experimental observation of the quantum Hall effect and Berry's phase in graphene. Nature 2005; 438: 201–4. - PubMed
-
- Radisavljevic B, Radenovic A, Brivio Jet al. . Single-layer MoS2 transistors. Nat Nanotechnol 2011; 6: 147–50. - PubMed
-
- Zafar A, Zafar Z, Zhao Wet al. . Sulfur-mastery: precise synthesis of 2D transition metal dichalcogenides. Adv Funct Mater 2019; 29: 1809261.
-
- Efetov DK, Wang L, Handschin Cet al. . Specular interband Andreev reflections at van der Waals interfaces between graphene and NbSe2. Nat Phys 2016; 12: 328–32.
