Evolutionary drivers of the hump-shaped latitudinal gradient of benthic polychaete species richness along the Southeastern Pacific coast
- PMID: 34692242
- PMCID: PMC8483006
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12010
Evolutionary drivers of the hump-shaped latitudinal gradient of benthic polychaete species richness along the Southeastern Pacific coast
Abstract
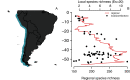
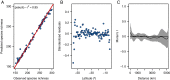
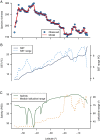
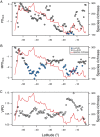
Latitudinal diversity gradients (LDG) and their explanatory factors are among the most challenging topics in macroecology and biogeography. Despite of its apparent generality, a growing body of evidence shows that 'anomalous' LDG (i.e., inverse or hump-shaped trends) are common among marine organisms along the Southeastern Pacific (SEP) coast. Here, we evaluate the shape of the LDG of marine benthic polychaetes and its underlying causes using a dataset of 643 species inhabiting the continental shelf (<200 m depth), using latitudinal bands with a spatial resolution of 0.5°, along the SEP (3-56° S). The explanatory value of six oceanographic (Sea Surface Temperature (SST), SST range, salinity, salinity range, primary productivity and shelf area), and one macroecological proxy (median latitudinal range of species) were assessed using a random forest model. The taxonomic structure was used to estimate the degree of niche conservatism of predictor variables and to estimate latitudinal trends in phylogenetic diversity, based on three indices (phylogenetic richness (PDSES), mean pairwise distance (MPDSES), and variation of pairwise distances (VPD)). The LDG exhibits a hump-shaped trend, with a maximum peak of species richness at ca. 42° S, declining towards northern and southern areas of SEP. The latitudinal pattern was also evident in local samples controlled by sampling effort. The random forest model had a high accuracy (pseudo-r2 = 0.95) and showed that the LDG could be explained by four variables (median latitudinal range, SST, salinity, and SST range), yet the functional relationship between species richness and these predictors was variable. A significant degree of phylogenetic conservatism was detected for the median latitudinal range and SST. PDSES increased toward the southern region, whereas VPD showed the opposite trend, both statistically significant. MPDSES has the same trend as PDSES, but it is not significant. Our results reinforce the idea that the south Chile fjord area, particularly the Chiloé region, was likely the evolutionary source of new species of marine polychaetes along SEP, creating a hotspot of diversity. Therefore, in the same way as the canonical LDG shows a decline in diversity while moving away from the tropics; on this case the decline occurs while moving away from Chiloé Island. These results, coupled with a strong phylogenetic signal of the main predictor variables suggest that processes operating mainly at evolutionary timescales govern the LDG.
Keywords: Annelida; Biogeography; Macroecology; Macroevolution; Niche conservatism; Random forest.
© 2021 Moreno et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Nicolás Rozbaczylo is employed by FAUNAMAR Ltda.
Figures

References
-
- Assis J, Tyberghein L, Bosch S, Verbruggen H, Serrão EA, De Clerck O. Bio-ORACLE v2. 0: extending marine data layers for bioclimatic modelling. Global Ecology and Biogeography. 2018;27(3):277–284. doi: 10.1111/geb.12693. - DOI
-
- Astorga A, Fernández M, Boschi EE, Lagos N. Two oceans, two taxa and one mode of development: latitudinal diversity patterns of South American crabs and test for possible causal processes. Ecology Letters. 2003;6(5):420–427. doi: 10.1046/j.1461-0248.2003.00445.x. - DOI
-
- Azovsky A, Garlitska L, Chertoprud E. Multi-scale taxonomic diversity of marine harpacticoids: does it differ at high and low latitudes? Marine Biology. 2016;163(5):94. doi: 10.1007/s00227-016-2876-0. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

