Reduced Intensity Conditioning Followed by Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Is a Good Choice for Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 34692485
- PMCID: PMC8529065
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.708727
Reduced Intensity Conditioning Followed by Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Is a Good Choice for Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Background: Reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) before allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) has been reported to have the same overall survival (OS) as myeloablative conditioning (MAC) for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in complete remission (CR) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). However, results from different studies are conflicting. Therefore, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis guided by PRISMA 2009 to confirm the efficacy and safety of RIC vs. MAC for AML in CR and MDS.
Methods: We search PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Cochrane central, clinical trial registries and related websites, major conference proceedings, and field-related journals from January 1, 1980, to July 1, 2020, for studies comparing RIC with MAC before the first allo-HSCT in patients with AML in CR or MDS. Only randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included. OS was the primary endpoint and generic inverse variance method was used to combine hazard ratio (HR) and 95% CI.
Results: We retrieved 7,770 records. Six RCTs with 1,413 participants (711 in RIC, 702 in MAC) were included. RIC had the same OS (HR = 0.95, 95% CI 0.64-1.4, p = 0.80) and cumulative incidence of relapse as MAC (HR = 1.18, 95% CI 0.88-1.59, p = 0.28). Furthermore, RIC significantly reduced non-relapse mortality more than total body irradiation/busulfan-based MAC (HR = 0.53, 95% CI 0.36-0.80, p = 0.002) and had similar long-term OS and graft failure as MAC.
Conclusion: RIC conditioning regimens are recommended as an adequate option of preparative treatment before allo-HSCT for patients with AML in CR or MDS.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/display_record.php?RecordID=185436.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia; myelodysplastic syndrome; non-relapse mortality (NRM); overall survival; reduced intensity conditioning (RIC).
Copyright © 2021 Song, Yin, Ding and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

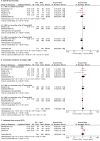
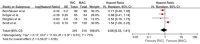
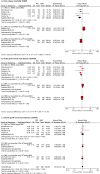
References
-
- Marks DI, Cullis JO, Ward KN, Lacey S, Syzdlo R, Hughes TP, et al. . Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Using Sibling and Volunteer Unrelated Donors. A Comparison of Complications in the First 2 Years. Ann Intern Med (1993) 119:207–14. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-119-3-199308010-00005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Martino R, Iacobelli S, Brand R, Jansen T, van Biezen A, Finke J, et al. . Retrospective Comparison of Reduced-Intensity Conditioning and Conventional High-Dose Conditioning for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Using HLA-Identical Sibling Donors in Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Blood (2006) 108:836–46. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-11-4503 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sugita J, Kagaya Y, Miyamoto T, Shibasaki Y, Nagafuji K, Ota S, et al. . Myeloablative and Reduced-Intensity Conditioning in HLA-Haploidentical Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation Using Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide. Bone Marrow Transplant (2019) 54:432–41. doi: 10.1038/s41409-018-0279-1 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

