Gambogenic Acid Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Colorectal Cancer via the Aurora A Pathway
- PMID: 34692693
- PMCID: PMC8526855
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.736350
Gambogenic Acid Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Colorectal Cancer via the Aurora A Pathway
Abstract
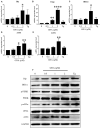
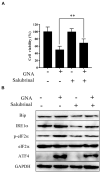
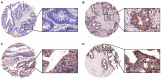
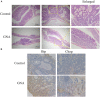
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignancies in the world and has a poor prognosis. In the present research, gambogenic acid (GNA), isolated from the traditional Chinese medicine gamboge, markedly induced apoptosis and inhibited the proliferation of CRC in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, GNA triggered endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, which subsequently activated inositol-requiring enzyme (IRE) 1α and the eukaryotic translation initiation factor (eIF) 2α pathway. Pretreatment with salubrinal (an eIF2α inhibitor) rescued GNA-induced cell death. Furthermore, GNA downregulated the expression of Aurora A. The Aurora A inhibitor alisertib decreased ER stress. In human colorectal adenocarcinoma tissue, Aurora A was upregulated compared to normal colorectal epithelial nuclei. Furthermore, GNA ameliorated mouse colitis-associated cancer models. Our findings demonstrated that GNA significantly inhibited the proliferation of CRC through activation of ER stress by regulating Aurora A, which indicates the potential of GNA for preventing the progression of CRC.
Keywords: Aurora A; colorectal cancer; endoplasmic reticulum stress; eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α; gambogenic acid.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Xu, Guo, Chen, Qian, Zhang, Zhou and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Albayrak D., Doganlar O., Erdogan S., Merakli M., Dogan A., Turker P., et al. (2021). Naringin combined with NF-kappa B inhibition and endoplasmic reticulum stress induces apoptotic cell death via oxidative stress and the PERK/eIF2 alpha/ATF4/CHOP axis in HT29 colon cancer cells. Biochem. Genet. 59 159–184. 10.1007/s10528-020-09996-5 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

