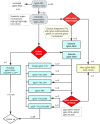
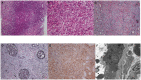
Clinicopathological Patterns and Predictors of the Functional Restoration of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Kidney Disease: A Chinese Single-Center Cohort Study
- PMID: 34692728
- PMCID: PMC8526789
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.736098
Clinicopathological Patterns and Predictors of the Functional Restoration of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Kidney Disease: A Chinese Single-Center Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic immunoreactivity-based fibro-inflammatory disease. Immunoglobulin G4-related kidney disease (IgG4-RKD) is a frequently overlooked diagnosis. This study aimed to describe IgG4-RKD and examine the factors relevant to the renal outcomes of IgG4-RD. Methods: We studied a prospective IgG4-RKD cohort between January 2012 and December 2020 with close follow-up. Clinicopathologic data at kidney biopsy were collected and analyzed. We aimed to explore independent risk factors for long-term renal outcome and disease relapse. Patients with an eGFR<45 ml/min per 1.73m2 at 12 months were defined as having poor outcomes. Results: The included 42 patients with IgG4-RKD had a mean age of 58.5 ± 8.7 years (male-to-female ratio = 5:1). The IgG4-RD responder index (RI) was 12.2 ± 3.3. A total of 66.7% of the patients presented with acute on kidney disease or acute on chronic kidney disease. Eight patients (19.0%) showed nephrotic-range proteinuria, and nine (21.4%) had high-titer IgG4-autoantibodies, including antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody and anti-phospholipase A2 receptor. A kidney biopsy was conducted in 40 patients. Thirty-seven (90.0%) patients were diagnosed with IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis, and 19 (47.5%) of them had concurrent glomerular diseases (membranous nephropathy [MN], n = 3; crescentic glomerulonephritis [CrGN], n = 11; diabetic kidney disease, n = 3; and both MN and CrGN, n = 2). IgG4-RD RI had a close relationship with serum C3 (R = -0.509, P = 0.001), C4 (R = -0.314, P = 0.049) levels, and peripheral blood eosinophil count (PBEC; R = 0.377, P = 0.024), factors that were not included in RI scores. Correlation analysis disclosed that IgG4-RD RI (R = 0.422, P = 0.007), organs involved (R = 0.452, P = 0.003), and C3 (R = -0.487, R = 0.002) were correlated with the percentage decrease of serum creatinine at 1 month. However, multivariate regression analysis failed to identify any clinicopathological parameters that could predict short-term renal restoration and IgG4-RKD relapse. Ten out of 29 variables, of most importance, were identified by the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression analysis. By multivariate logistic regression a higher serum IgG4 (OR = 0.671, P = 0.010), IgG1 (OR = 1.396, P = 0.049), IgG3 (OR = 19.154, P = 0.039), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR; OR = 1.042, P = 0.032) were found to be independent factors for poor long-term outcome. Conventional immunosuppressive medications and/or rituximab were prescribed, and in 83.3% of the patients, the kidney function improved. Repeat kidney biopsies confirmed the remission of interstitial inflammation in two patients under immunosuppressive therapy. However, the disease relapse rate was as high as 31.0%. Conclusions: We strongly recommend a kidney biopsy in active IgG4-RD, especially when there is proteinuria and renal dysfunction, because concurrent glomerular involvement and active interstitial inflammation should be assessed. A higher serum IgG1, IgG3, and ESR were independent factors for the poor long-term renal outcome; however, elevated IgG4 predicted a good renal prognosis, and appropriate and timely immunosuppressive therapy can help achieve a better prognosis.
Keywords: IgG4 autoantibodies; IgG4-related disease; crescentic nephritis; kidney disease; membranous nephropathy; prognosis; tubulointerstitial nephritis.
Copyright © 2021 Su, Wang, Wang and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IgG4-related kidney disease: Clinicopathologic features, differential diagnosis, and mimics.Semin Diagn Pathol. 2024 Mar;41(2):88-94. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2023.12.001. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38246802 Review.
-
IgG4-related kidney disease: experience from a Mexican cohort.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Nov;39(11):3401-3408. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05135-y. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32488771
-
[Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of IgG4-related kidney disease].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Aug 24;101(32):2559-2562. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20201222-03434. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34407583 Chinese.
-
Role of complement system in patients with biopsy-proven immunoglobulin G4-related kidney disease.Hum Pathol. 2018 Nov;81:220-228. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2018.07.008. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Hum Pathol. 2018. PMID: 30031099
-
IgG4-related kidney disease (IgG4-RKD) with membranous nephropathy as its initial manifestation: report of one case and literature review.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Jul 16;20(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1419-6. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31311519 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Evaluation of Antiphospholipase A2 Receptor IgG4 level and Its IgG4-to-IgG Ratio Based on Quantitative Immunoassays in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy.Biomed Res Int. 2022 May 13;2022:9127520. doi: 10.1155/2022/9127520. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35782060 Free PMC article.
-
IgG4-related disease complicated by PLA2R-associated membranous nephropathy: A case report.Open Life Sci. 2024 Jul 25;19(1):20220921. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0921. eCollection 2024. Open Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39071497 Free PMC article.
-
Current and future advances in practice: IgG4-related disease.Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2024 Apr 10;8(2):rkae020. doi: 10.1093/rap/rkae020. eCollection 2024. Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2024. PMID: 38601138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact on the scientific community of the 2018 addendum to the CHCC.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 1;9:1081063. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1081063. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36530898 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
IgG4-Related Membranous Nephropathy After COVID-19 Vaccination: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Mar 12;16(3):e56028. doi: 10.7759/cureus.56028. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38606210 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous