Mechanisms of Action of MiRNAs and LncRNAs in Extracellular Vesicle in Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 34692785
- PMCID: PMC8531438
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.733985
Mechanisms of Action of MiRNAs and LncRNAs in Extracellular Vesicle in Atherosclerosis
Abstract
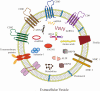
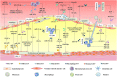
Atherosclerosis, a complex chronic inflammatory disease, involves multiple alterations of diverse cells, including endothelial cells (ECs), vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells (DCs), platelets, and even mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Globally, it is a common cause of morbidity as well as mortality. It leads to myocardial infarctions, stroke and disabling peripheral artery disease. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are a heterogeneous group of cell-derived membranous structures that secreted by multiple cell types and play a central role in cell-to-cell communication by delivering various bioactive cargos, especially microRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). Emerging evidence demonstrated that miRNAs and lncRNAs in EVs are tightly associated with the initiation and development of atherosclerosis. In this review, we will outline and compile the cumulative roles of miRNAs and lncRNAs encapsulated in EVs derived from diverse cells in the progression of atherosclerosis. We also discuss intercellular communications via EVs. In addition, we focused on clinical applications and evaluation of miRNAs and lncRNAs in EVs as potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for atherosclerosis.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; endothelial cells; extracellular vesicles; long non-coding RNA; microRNA; vascular smooth muscle cells.
Copyright © 2021 Xu, Ni and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles in atherosclerosis and vascular calcification: the versatile non-coding RNAs from endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 4;10:1193660. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1193660. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37469665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Extracellular Vesicles From Multiple Cells on Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 10;13:857331. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.857331. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35620296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-to-cell communication: microRNAs as hormones.Mol Oncol. 2017 Dec;11(12):1673-1686. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12144. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Mol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29024380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial extracellular vesicles modulate the macrophage phenotype: Potential implications in atherosclerosis.Scand J Immunol. 2018 Apr;87(4):e12648. doi: 10.1111/sji.12648. Scand J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29465752
-
Extracellular vesicles and their non-coding RNA cargos: Emerging players in cardiovascular disease.J Physiol. 2023 Nov;601(22):4989-5009. doi: 10.1113/JP283200. Epub 2022 Sep 29. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36094621 Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate the Progression of Atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- Mice via FENDRR.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2022 Jun;22(6):528-544. doi: 10.1007/s12012-022-09736-8. Epub 2022 Mar 27. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35344140
-
Comparative Analysis of Differentially Expressed Circular RNAs in Polarized Macrophages.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 16;13:823517. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.823517. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35368656 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA: A Novel Insight into the Pathogenesis of Acute Lung Injury.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 11;12(2):604. doi: 10.3390/jcm12020604. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36675533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A potential mechanism for the cytoprotective effects of activated protein C-released endothelial extracellular vesicles.Blood. 2024 Apr 18;143(16):1670-1675. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023023518. Blood. 2024. PMID: 38427750 Free PMC article.
-
A Potential Target for Diabetic Vascular Damage: High Glucose-Induced Monocyte Extracellular Vesicles Impair Endothelial Cells by Delivering miR-142-5p.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 May 9;10:913791. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.913791. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35615474 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

