Machine learning applications for therapeutic tasks with genomics data
- PMID: 34693370
- PMCID: PMC8515011
- DOI: 10.1016/j.patter.2021.100328
Machine learning applications for therapeutic tasks with genomics data
Abstract
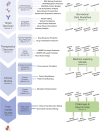
Thanks to the increasing availability of genomics and other biomedical data, many machine learning algorithms have been proposed for a wide range of therapeutic discovery and development tasks. In this survey, we review the literature on machine learning applications for genomics through the lens of therapeutic development. We investigate the interplay among genomics, compounds, proteins, electronic health records, cellular images, and clinical texts. We identify 22 machine learning in genomics applications that span the whole therapeutics pipeline, from discovering novel targets, personalizing medicine, developing gene-editing tools, all the way to facilitating clinical trials and post-market studies. We also pinpoint seven key challenges in this field with potentials for expansion and impact. This survey examines recent research at the intersection of machine learning, genomics, and therapeutic development.
Keywords: genomics; machine learning; therapeutics discovery and development.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interests declared.
Figures










Comment in
-
AI in drug discovery: Applications, opportunities, and challenges.Patterns (N Y). 2022 Jun 10;3(6):100529. doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2022.100529. eCollection 2022 Jun 10. Patterns (N Y). 2022. PMID: 35755871 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hieter P., Boguski M. Functional genomics: it’s all how you read it. Science. 1997;278:601–602. - PubMed
-
- Wong M.-L., Licinio J. From monoamines to genomic targets: a paradigm shift for drug discovery in depression. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004;3:136–151. - PubMed
-
- Chin L., Andersen J.N., Futreal P.A. Cancer genomics: from discovery science to personalized medicine. Nat. Med. 2011;17:297. - PubMed
-
- Hamburg M.A., Collins F.S. The path to personalized medicine. New Engl. J. Med. 2010;363:301–304. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

