The reliability and validity of triceps surae muscle volume assessment using freehand three-dimensional ultrasound in typically developing infants
- PMID: 34693531
- PMCID: PMC8819047
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.13565
The reliability and validity of triceps surae muscle volume assessment using freehand three-dimensional ultrasound in typically developing infants
Abstract
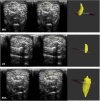
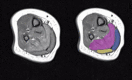
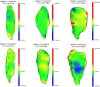
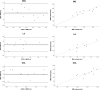
This study assessed the intra-acquirer, intra- and inter-processor reliability, and validity of the in vivo assessment of the medial gastrocnemius (MG), lateral gastrocnemius (LG) and soleus (SOL) muscle volumes using freehand 3D ultrasound (3DUS) in typically developing infants. Reliability assessments of freehand 3DUS were undertaken in infants across three ages groups: three, six and twelve months of age, with validity testing completed against magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in infants at 3 months of age. Freehand 3DUS scanning was carried out by a single acquirer, with two independent processors manually segmenting images to render volumes. MRI images were segmented independently by a separate processor, with the volumes compared to those obtained via freehand 3DUS. Reliability was assessed using intraclass correlation (ICC), coefficient of variance (CV) and minimal detectable change (MDC) across each assessment time point. Validity was assessed using the limits of agreement. ICCs for intra-acquirer reliability of the acquisition process for freehand 3DUS ranged from 0.91 to 0.99 across all muscles. ICCs for intra-processor and inter-processor reliability for the segmentation process of freehand 3DUS ranged from 0.80 to 0.98 across all muscles. Acceptable levels of agreement between muscle volume obtained by freehand 3DUS and MRI were found for all muscles; however, freehand 3DUS overestimated muscle volume of MG and LG and underestimate the SOL compared with MRI, with average absolute differences of MG = 0.3 ml, LG = 0.3 ml and Sol = 1.2 ml. Freehand 3DUS is a reliable method for measuring in vivo triceps surae muscle volume in typically developing infants. We conclude that freehand 3DUS is a useful tool to assess changes in muscle volume in response to growth and interventions in infants.
Keywords: child; muscle volume; reliability; statistical shape modelling; ultrasound; validity.
© 2021 Anatomical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, either real or perceived.
Figures
References
-
- Agur, A.M. , Ng‐Thow‐Hing, V. , Ball, K.A. , Fiume, E. & McKee, N.H. (2003) Documentation and three‐dimensional modelling of human soleus muscle architecture. Clinical Anatomy, 16(4), 285–293. - PubMed
-
- Barber, L. , Barrett, R. & Lichtwark, G. (2009) Validation of a freehand 3D ultrasound system for morphological measures of the medial gastrocnemius muscle. Journal of Biomechanics, 42(9), 1313–1319. - PubMed
-
- Barber, L. , Hastings‐Ison, T. , Baker, R. , Kerr Graham, H. , Barrett, R. & Lichtwark, G. (2013) The effects of botulinum toxin injection frequency on calf muscle growth in young children with spastic cerebral palsy: a 12‐month prospective study. Journal of Children's Orthopaedics, 7(5), 425–433. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barrett, R.S. & Lichtwark, G.A. (2010) Gross muscle morphology and structure in spastic cerebral palsy: a systematic review. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 52(9), 794–804. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

