Brief Report: No Differences Between Lopinavir/Ritonavir and Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor-Based Antiretroviral Therapy on Clearance of Plasmodium falciparum Subclinical Parasitemia in Adults Living With HIV Starting Treatment (A5297)
- PMID: 34693933
- PMCID: PMC9425486
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002839
Brief Report: No Differences Between Lopinavir/Ritonavir and Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor-Based Antiretroviral Therapy on Clearance of Plasmodium falciparum Subclinical Parasitemia in Adults Living With HIV Starting Treatment (A5297)
Abstract
Background: HIV protease inhibitors anti-Plasmodium falciparum activity in adults remains uncertain.
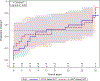
Methods: Adults with HIV CD4+ counts >200 cells/mm3 starting antiretroviral therapy (ART) with P. falciparum subclinical parasitemia (Pf SCP) were randomized 1:1 to (step 1) protease inhibitor lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/r)-based (arm A) or nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (nNRTI)-based ART (arm B) for 15 days. In step 2, participants received nNRTI-based ART and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis for 15 days. P. falciparum SCP clearance was measured by polymerase chain reaction. The Fisher exact test [95% exact confidence interval (CI)] was used to compare proportions of P. falciparum SCP clearance (<10 parasites/μL on 3 occasions within 24 hours) between LPV/r and nNRTI arms at day 15. The Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test were used to compare time-to-clearance.
Results: Fifty-two adults from Kenya, Malawi, and Uganda with a median age = 31 (Q1, Q3: 24-39) years, 33% women, with baseline median CD4+ counts of 324 (259-404) cells/mm3, median HIV-1 RNA viremia of 5.18 log10 copies/mL (4.60-5.71), and median estimated P. falciparum density of 454 parasites/μL (83-2219) enrolled in the study. Forty-nine (94%) participants completed the study. At day 15, there was no statistically significant difference in the proportions of P. falciparum SCP clearance between the LPV/r (23.1% clearance; 6 of the 26) and nNRTI (26.9% clearance; 7 of the 26) arms [between-arm difference 3.9% (95% CI, -21.1% to 28.4%; P = 1.00)]. No significant difference in time-to-clearance was observed between the arms (P = 0.80).
Conclusions: In a small randomized study of adults starting ART with P. falciparum SCP, no statistically significant differences were seen between LPV/r- and nNRTI-based ART in P. falciparum SCP clearance after 15 days of treatment.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01632891.
Copyright © 2021 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS 2019 Data. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) 2019 June 26, 2020; Available from: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2019/2019-UNAIDS-data. Accessed November 15, 2020.
-
- World Malaria Report 2019. June 26, 2020; Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565721. Accessed November 15, 2020.
-
- Flateau C, Le Loup G, and Pialoux G, Consequences of HIV infection on malaria and therapeutic implications: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis, 2011. 11(7): p. 541–56. - PubMed
-
- Update on the recommendations on first- and second- line antiretroviral therapy regimens. June 26, 2020; World Health Organization. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/325892/WHO-CDS-HIV-19.1.... Accessed November 15, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials