3D Harmonic and Subharmonic Imaging for Characterizing Breast Lesions: A Multi-Center Clinical Trial
- PMID: 34694019
- PMCID: PMC9884499
- DOI: 10.1002/jum.15848
3D Harmonic and Subharmonic Imaging for Characterizing Breast Lesions: A Multi-Center Clinical Trial
Abstract
Objective: Breast cancer is the most frequent type of cancer among women. This multi-center study assessed the ability of 3D contrast-enhanced ultrasound to characterize suspicious breast lesions using clinical assessments and quantitative parameters.
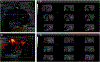
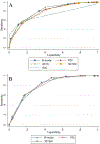
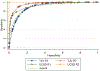
Methods: Women with suspicious breast lesions scheduled for biopsy were enrolled in this prospective, study. Following 2D grayscale ultrasound and power Doppler imaging (PDI), a contrast agent (Definity; Lantheus) was administrated. Contrast-enhanced 3D harmonic imaging (HI; transmitting/receiving at 5.0/10.0 MHz), as well as 3D subharmonic imaging (SHI; transmitting/receiving at 5.8/2.9 MHz), were performed using a modified Logiq 9 scanner (GE Healthcare). Five radiologists independently scored the imaging modes (including standard-of-care imaging) using a 7-point BIRADS scale as well as lesion vascularity and diagnostic confidence. Parametric volumes were constructed from time-intensity curves for vascular heterogeneity, perfusion, and area under the curve. Diagnostic accuracy was determined relative to pathology using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) and reverse, step-wise logistical regression analyses. The κ-statistic was calculated for inter-reader agreement.
Results: Data were successfully acquired in 219 cases and biopsies indicated 164 (75%) benign and 55 (25%) malignant lesions. SHI depicted more anastomoses and vascularity than HI (P < .021), but there were no differences by pathology (P > .27). Ultrasound achieved accuracies of 82 to 85%, which was significantly better than standard-of-care imaging (72%; P < .03). SHI increased diagnostic confidence by 3 to 6% (P < .05), but inter-reader agreements were medium to low (κ < 0.52). The best regression model achieved 97% accuracy by combining clinical reads and parametric SHI.
Conclusions: Combining quantitative 3D SHI parameters and clinical assessments improves the characterization of suspicious breast lesions.
Keywords: 3D ultrasound imaging; breast cancer; contrast-enhanced ultrasound; harmonic imaging; subharmonic imaging.
© 2021 American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 2018; 71:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Heer E, Harper A, Escandor N, Sung H, McCormack V, Fidler-Benaoudia MM. Global burden and trends in premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancer: a population-based study. Lancet Glob Health 2020; 8:e1027–e1037. - PubMed

