Association Between Local Anesthetic Dosing, Postoperative Opioid Requirement, and Pain Scores After Lumpectomy and Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy with Multimodal Analgesia
- PMID: 34694521
- PMCID: PMC11110646
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-021-10981-4
Association Between Local Anesthetic Dosing, Postoperative Opioid Requirement, and Pain Scores After Lumpectomy and Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy with Multimodal Analgesia
Abstract
Background: Multimodal analgesia (MMA) during breast surgery reduces postoperative pain and opioid requirements, but the relative contribution of local anesthetic dosing as a component of MMA is not well defined among patients undergoing lumpectomy and sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB).
Patients and methods: We identified consecutive patients who underwent lumpectomy and SLNB with MMA from 1/2019 to 4/2020. Univariable and multivariable linear and logistic regression were used to examine associations between local anesthetics, opioid requirements in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU), and pain scores in the PACU and on postoperative day (POD) 1.
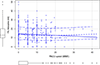
Results: In total, 1603 patients [median tumor size, 14 mm (interquartile range 8-20 mm)] were included. The median PACU opioid requirement was 0 morphine milligram equivalents (interquartile range 0-5). PACU maximum pain was none or mild in 58% of patients and moderate to severe in 42%; among 420 survey respondents, 56% reported no or mild pain and 44% reported moderate to severe pain on POD 1. On multivariable analysis that adjusted for routine components of MMA, increasing doses of 0.5% bupivacaine were associated with reduced PACU opioid requirements (β -0.04, 95% confidence interval -0.07 to -0.01, p = 0.011) and lower odds of moderate to severe pain (odds ratio 0.98, 95% confidence interval 0.97-0.99, p < 0.001). Local anesthetics were not associated with pain scores on POD 1.
Conclusions: Higher amounts of local anesthetics reduce acute postoperative pain and opioid requirement after lumpectomy and SLNB. Maximizing dosing within weight-based limits is a low-risk, cost-effective pain control strategy that can be used in diverse practice settings.
© 2021. Society of Surgical Oncology.
Figures

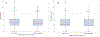
References
-
- Beverly A, Kaye AD, Ljungqvist O, Urman RD. Essential elements of multimodal analgesia in enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) guidelines. Anesthesiol Clin. 2017;35(2):e115–e143. - PubMed
-
- Rojas KE, Manasseh DM, Flom PL, et al. A pilot study of a breast surgery enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocol to eliminate narcotic prescription at discharge. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018;171(3):621–626. - PubMed
-
- Egan KG, De Souza M, Muenks E, Nazir N, Korentager R. Opioid consumption following breast surgery decreases with a brief educational intervention: A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020;27(9):3156–3162. - PubMed
-
- Brenin DR, Dietz JR, Baima J, et al. Pain management in breast surgery: Recommendations of a multidisciplinary expert panel-the american society of breast surgeons. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020;27(12):4588–4602. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

