The Use of Intraoperative Digital Radiography Alignment Software to Assess Implant Placement in Total Hip Arthroplasty
- PMID: 34694562
- PMCID: PMC8733135
- DOI: 10.1007/s12178-021-09722-7
The Use of Intraoperative Digital Radiography Alignment Software to Assess Implant Placement in Total Hip Arthroplasty
Abstract
Purpose of review: Total hip arthroplasty (THA) is a highly successful surgery with growing rates of utilization in the USA, but surgical outliers leading to postoperative complications remain a concern. There is need for a standard system of accurate, predictable intraoperative evaluation to decrease component positioning outliers. Many current intraoperative imaging systems have shown promise, but there are drawbacks that have led to slow adoption. Digital radiography, in conjunction with Radlink™ technology, is a potential solution to this problem. This review summarizes the clinical application and scientific literature regarding the use of Radlink™ in THA.
Recent findings: Traditional surgeon-directed component placement can result in surgical outliers. This is especially true not only among low-volume arthroplasty surgeons, but can also occur with experienced, high-volume surgeons. Digital radiography allows for more precise and accurate placement of the acetabular cup in a targeted range in an effort to improve THA outcomes. Intraoperative images are obtained quickly, and they are accurate when compared to postoperative images. Additionally, the use of Radlink™ results in a significant decrease in leg length and femoral offset outliers. The adoption of Radlink™ technology in THA can significantly decrease surgical outliers, especially errors in acetabular cup placement, leg length, and femoral offset. Digital radiography avoids many of the previous aversions to intraoperative imaging as it produces a fast, reliable image with little radiation exposure and minimal interruption to workflow. There is the potential for Radlink™ use to provide superior patient outcomes, as a decrease in surgical outliers can minimize implant malpositioning with resultant need for revision THAs. Radlink™ may also provide benefit in analyzing other parameters, such as component sizing.
Keywords: Component positioning; Digital radiography; Intraoperative imaging; Radlink; Total hip arthroplasty.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Jacob Siebenmorgen declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Jeff Stambough discloses the following conflicts: American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons: Board or committee member; American Joint Replacement Registry (AJRR): Board or committee member; Journal of Arthroplasty: Editorial or governing board; Bone and Joint 360: Editorial or governing board; Signature Orthopaedics: IP royalties; Smith & Nephew: Paid consultant.
Benjamin Stronach discloses the following conflicts: American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons: Board or committee member; Bone and Joint 360: Editorial or governing board; Signature Orthopaedics: IP royalties; Tightline Development: IP royalties; Pacific Research: IP royalties; DJO Global: Paid consultant.
Simon Mears discloses the following conflicts: American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons, Fragility Fracture Network: Board or committee member, Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehabilitation, Journal of the American Geriatrics Society: Editorial or governing board; Delta Orthopedics, Stock
Simon C. Mears discloses Medical/Orthopaedic publications editorial/governing board (The following conflicts were disclosed) Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehabilitation.
Board member/committee appointments for a society (The following conflicts were disclosed) International Geriatric Fracture Society
Figures

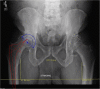
Similar articles
-
Intra-operative digital imaging: assuring the alignment of components when undertaking total hip arthroplasty.Bone Joint J. 2018 Jan;100-B(1 Supple A):36-43. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.100B1.BJJ-2017-0596.R1. Bone Joint J. 2018. PMID: 29292338 Free PMC article.
-
Value of 3D Preoperative Planning for Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Based on Biplanar Weightbearing Radiographs.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Mar 10;2019:1932191. doi: 10.1155/2019/1932191. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30984776 Free PMC article.
-
Digital Radiography in Total Hip Arthroplasty: Technique and Radiographic Results.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018 Feb 7;100(3):226-235. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.16.01501. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018. PMID: 29406344
-
Intraoperative imaging in hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized controlled trials and observational studies.Arthroplasty. 2023 Apr 7;5(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s42836-023-00173-8. Arthroplasty. 2023. PMID: 37024967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The current role of robotics in total hip arthroplasty.EFORT Open Rev. 2019 Nov 1;4(11):618-625. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.4.180088. eCollection 2019 Nov. EFORT Open Rev. 2019. PMID: 31754468 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Achieving Precise Cup Positioning in Direct Anterior Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Narrative Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Jan 31;59(2):271. doi: 10.3390/medicina59020271. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 36837472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tri-Lock Bone Preservation Stem Versus Conventional Corail Stem in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty via Direct Anterior Approach: A Short-Term, Retrospective, Comparative Study.Med Sci Monit. 2023 Apr 17;29:e939635. doi: 10.12659/MSM.939635. Med Sci Monit. 2023. PMID: 37062914 Free PMC article.
-
Imageless vs Image-Based Computer Navigation in Total Hip Arthroplasty: An Intracase Comparison Shows Variability Between Technologies.Arthroplast Today. 2025 May 12;33:101707. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2025.101707. eCollection 2025 Jun. Arthroplast Today. 2025. PMID: 40485815 Free PMC article.
-
Managing early complications in total hip arthroplasty: the safety of immediate revision.J Orthop Traumatol. 2023 Jul 31;24(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s10195-023-00719-1. J Orthop Traumatol. 2023. PMID: 37525070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berry DJ, Harmsen WS, Cabanela ME, Morrey BF. Twenty-five-year survivorship of two thousand consecutive primary Charnley total hip replacements: Factors affecting survivorship of acetabular and femoral components. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery - Series A. 2002;84:171–177. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200202000-00002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

