Polycaprolactone/gelatin electrospun nanofibres containing biologically produced tellurium nanoparticles as a potential wound dressing scaffold: Physicochemical, mechanical, and biological characterisation
- PMID: 34694673
- PMCID: PMC8675828
- DOI: 10.1049/nbt2.12020
Polycaprolactone/gelatin electrospun nanofibres containing biologically produced tellurium nanoparticles as a potential wound dressing scaffold: Physicochemical, mechanical, and biological characterisation
Abstract
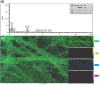
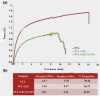
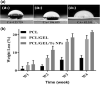
The biologically synthesised tellurium nanoparticles (Te NPs) were applied in the fabrication of Te NP-embedded polycaprolactone/gelatin (PCL/GEL) electrospun nanofibres and their antioxidant and in vivo wound healing properties were determined. The as-synthesised nanofibres were characterised using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy and elemental mapping, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The mechanical properties and surface hydrophobicity of scaffolds were investigated using tensile analysis and contact angle tests, respectively. The biocompatibility of the produced scaffolds on mouse embryonic fibroblast cells (3T3) was evaluated using MTT assay. The highest wound healing activity (score 15/19) was achieved for scaffolds containing Te NPs. The wounds treated with PCL/GEL/Te NPs had inflammation state equal to the positive control. Also, the mentioned scaffold represented positive effects on collagen formation and collagen fibre's horizontalisation in a dose-dependent manner. The antioxidative potency of Te NP-containing scaffolds was demonstrated with lower levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and catalase (∼3 times) and a higher level of glutathione (GSH) (∼2 times) in PCL/GEL/Te NP-treated samples than the negative control. The obtained results strongly demonstrated the healing activity of the produced nanofibres, and it can be inferred that scaffolds containing Te NPs are suitable for wound dressing.
© 2021 The Authors. IET Nanobiotechnology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Institution of Engineering and Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



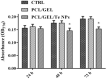



References
-
- Ahmed, R. , et al.: Novel electrospun chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/zinc oxide nanofibrous mats with antibacterial and antioxidant properties for diabetic wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 120, 385–393 (2018) - PubMed
-
- Augustine, R. , et al.: Electrospun polycaprolactone membranes incorporated with Zno nanoparticles as skin substitutes with enhanced fibroblast proliferation and wound healing. Rsc. Adv. 4(47), 24777–24785 (2014)
-
- Akturk, O. , et al.: Wet electrospun silk fibroin/gold nanoparticle 3d matrices for wound healing applications. Rsc. Adv. 6(16), 13234–13250 (2016)
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

