Influence of seed coating with copper, iron and zinc nanoparticles on growth and yield of tomato
- PMID: 34694722
- PMCID: PMC8675844
- DOI: 10.1049/nbt2.12064
Influence of seed coating with copper, iron and zinc nanoparticles on growth and yield of tomato
Abstract
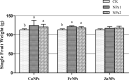
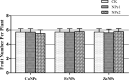
Neutral nanoparticles (NPs) of copper (Cu), iron (Fe) and zinc (Zn) are widely used in agriculture. Polymer seed coating with different metal NPs may supply important nutrients during plant growth and consequently enhances yields. In this research, three kinds of metal NPs were conducted to optimize the optimal concentration through seed coating for improving plant growth and productivity of tomato. Seeds of Venice tomato cultivars were coated by polymer-based mixture with different concentrations of Cu, Fe and Zn NPs, respectively. At harvest, seed germination, internode length, average weight of single fruit, yield and fruit shape index were measured. When compared with control, the internode length increased by 7.3% and 6.8% with low concentration of Fe NPs and Zn NPs, respectively. The average weight per fruit improved over control by 10.2% and 7.5% with low concentration of Cu NPs and Fe NPs, respectively. The yield with low concentration of Cu NPs and Fe NPs increased the yield by 10.7% and 6.5% compared with control. These results indicated that polymer seed coating with low concentration of metal NPs may promote the uptake of some nutrient and thus improve the productivity of tomato.
© 2021 The Authors. IET Nanobiotechnology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Institution of Engineering and Technology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tomato response to metal nanoparticles introduction into the nutrient medium.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020 Jul;14(5):382-388. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2019.0183. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32691740 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of seed priming with Selenium nanoparticles on germination and seedlings growth of tomato.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 20;14(1):6726. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57049-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38509209 Free PMC article.
-
Metal nanoparticles: Phytotoxicity on tomato and effect on symbiosis with the Fusarium solani FsK strain.Sci Total Environ. 2021 Sep 15;787:147606. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147606. Epub 2021 May 8. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 33991907
-
Fe-NPs and Zn-NPs: Advancing Aquaculture Performance Through Nanotechnology.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024 Jun;202(6):2828-2842. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03850-6. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024. PMID: 37723405 Review.
-
Diversity of copper-containing nanoparticles and their influence on plant growth and development.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2025 Mar;220:109575. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2025.109575. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39893945 Review.
Cited by
-
Carbon Nanodot-Microbe-Plant Nexus in Agroecosystem and Antimicrobial Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Jul 25;14(15):1249. doi: 10.3390/nano14151249. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39120354 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Elsharkawy, M. , et al.: Zinc oxide nanostructures as a control strategy of bacterial speck of tomato caused by Pseudomonas syringae in Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27, 19049–19057 (2020) - PubMed
-
- Rehman, A. , Farooq, M. : Zinc seed coating improves the growth, grain yield and grain biofortification of bread wheat. Acta Physiol. Plant. 38, 238 (2016)
-
- Deng, Q.X. , Zeng, D.F. : Physicochemical property testing of a novel maize seed coating agent and its antibacterial mechanism research. J. Soil Sci. 5, 45–52 (2015)
-
- Farooq, M. , Wahid, A. , Siddique, K.H.M. : Micronutrient application through seed treatments‐a review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 12, 125–142 (2012)
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

