The Small RNA MicC Downregulates hilD Translation To Control the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 Type III Secretion System in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium
- PMID: 34694902
- PMCID: PMC8765453
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00378-21
The Small RNA MicC Downregulates hilD Translation To Control the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 Type III Secretion System in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium
Abstract
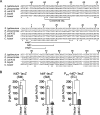
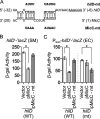
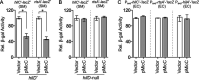
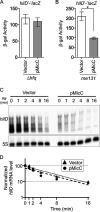
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium invades the intestinal epithelium and induces inflammatory diarrhea using the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI1) type III secretion system (T3SS). Expression of the SPI1 T3SS is controlled by three AraC-like regulators, HilD, HilC, and RtsA, which form a feed-forward regulatory loop that leads to activation of hilA, encoding the main transcriptional regulator of the T3SS structural genes. This complex system is affected by numerous regulatory proteins and environmental signals, many of which act at the level of hilD mRNA translation or HilD protein function. Here, we show that the sRNA MicC blocks translation of the hilD mRNA by base pairing near the ribosome binding site. MicC does not induce degradation of the hilD message. Our data indicate that micC is transcriptionally activated by SlyA, and SlyA feeds into the SPI1 regulatory network solely through MicC. Transcription of micC is negatively regulated by the OmpR/EnvZ two-component system, but this regulation is dependent on SlyA. OmpR/EnvZ control SPI1 expression partially through MicC but also affect expression through other pathways, including an EnvZ-dependent, OmpR-independent mechanism. MicC-mediated regulation plays a role during infection, as evidenced by an SPI1 T3SS-dependent increase in Salmonella fitness in the intestine in the micC deletion mutant. These results further elucidate the complex regulatory network controlling SPI1 expression and add to the list of sRNAs that control this primary virulence factor. IMPORTANCE The Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI1) type III secretion system (T3SS) is the primary virulence factor required for causing intestinal disease and initiating systemic infection. The system is regulated in response to a large variety of environmental and physiological factors such that the T3SS is expressed at only the appropriate time and place in the host during infection. Here, we show how the sRNA MicC affects expression of the system. This work adds to our detailed mechanistic studies aimed at a complete understanding of the regulatory circuit.
Keywords: EnvZ; MicC; OmpR; SPI1; Salmonella; SlyA.
Figures


Similar articles
-
HilD, HilC, and RtsA Form Homodimers and Heterodimers To Regulate Expression of the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island I Type III Secretion System.J Bacteriol. 2020 Apr 9;202(9):e00012-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00012-20. Print 2020 Apr 9. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32041797 Free PMC article.
-
PhoP-Mediated Repression of the SPI1 Type 3 Secretion System in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2019 Jul 24;201(16):e00264-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00264-19. Print 2019 Aug 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31182495 Free PMC article.
-
HilD, HilC and RtsA constitute a feed forward loop that controls expression of the SPI1 type three secretion system regulator hilA in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Aug;57(3):691-705. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04737.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16045614
-
Adaptation to the host environment: regulation of the SPI1 type III secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007 Feb;10(1):24-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.12.002. Epub 2007 Jan 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17208038 Review.
-
Salmonella invasion gene regulation: a story of environmental awareness.J Microbiol. 2005 Feb;43 Spec No:110-7. J Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15765064 Review.
Cited by
-
The Salmonella pathogenicity island 1-encoded small RNA InvR mediates post-transcriptional feedback control of the activator HilA in Salmonella.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 22:2024.11.21.624761. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.21.624761. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Bacteriol. 2025 Mar 20;207(3):e0049124. doi: 10.1128/jb.00491-24. PMID: 39605656 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Small RNAs Activate Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 by Modulating mRNA Stability through the hilD mRNA 3' Untranslated Region.J Bacteriol. 2023 Jan 26;205(1):e0033322. doi: 10.1128/jb.00333-22. Epub 2022 Dec 6. J Bacteriol. 2023. PMID: 36472436 Free PMC article.
-
The Salmonella pathogenicity island 1-encoded small RNA InvR mediates post-transcriptional feedback control of the activator HilA in Salmonella.J Bacteriol. 2025 Mar 20;207(3):e0049124. doi: 10.1128/jb.00491-24. Epub 2025 Feb 27. J Bacteriol. 2025. PMID: 40013798 Free PMC article.
-
O2-dependent incapacitation of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 repressor HilE.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Feb 18;15:1434254. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1434254. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40041146 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in sRNA-mediated regulation of Salmonella infection in the host.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 May 15;15:1503337. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1503337. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40444151 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

