Heart and Lung Sound Measurement Using an Esophageal Stethoscope with Adaptive Noise Cancellation
- PMID: 34695968
- PMCID: PMC8540990
- DOI: 10.3390/s21206757
Heart and Lung Sound Measurement Using an Esophageal Stethoscope with Adaptive Noise Cancellation
Abstract
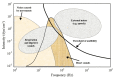
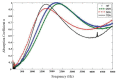
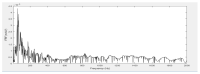
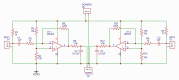
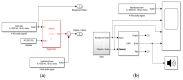
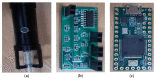
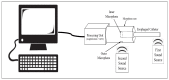
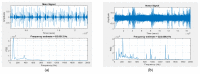
In surgeries where general anesthesia is required, the auscultation of heart and lung sounds is essential to provide information on the patient's cardiorespiratory system. Heart and lung sounds can be recorded using an esophageal stethoscope; however, there is huge background noise when this device is used in an operating room. In this study, a digital esophageal stethoscope system was designed. A 3D-printed case filled with Polydimethylsiloxane material was designed to hold two electret-type microphones. One of the microphones was placed inside the printed case to collect the heart and lung sound signals coming out from the patient through the esophageal catheter, the other was mounted on the surface of the case to collect the operating room sounds. A developed adaptive noise canceling algorithm was implemented to remove the operating room noise corrupted with the main heart and lung sound signals and the output signal was displayed on software application developed especially for this study. Using the designed case, the noise level of the signal was reduced to some extent, and by adding the adaptive filter, further noise reduction was achieved. The designed system is lightweight and can provide noise-free heart and lung sound signals.
Keywords: SIMULINK; adaptive noise canceling; digital esophageal stethoscope; esophageal catheter; least mean square.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures









Similar articles
-
A study of heart sound and lung sound separation by independent component analysis technique.Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006;2006:5708-11. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2006.260223. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006. PMID: 17945913
-
Development of a Finger-Ring-Shaped Hybrid Smart Stethoscope for Automatic S1 and S2 Heart Sound Identification.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Sep 20;21(18):6294. doi: 10.3390/s21186294. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34577501 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an Electronic Stethoscope and a Classification Algorithm for Cardiopulmonary Sounds.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 3;22(11):4263. doi: 10.3390/s22114263. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35684884 Free PMC article.
-
MEMS and ECM Sensor Technologies for Cardiorespiratory Sound Monitoring-A Comprehensive Review.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Oct 31;24(21):7036. doi: 10.3390/s24217036. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39517931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AI diagnosis of heart sounds differentiated with super StethoScope.J Cardiol. 2024 Apr;83(4):265-271. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2023.09.007. Epub 2023 Sep 20. J Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 37734656 Review.
Cited by
-
Tablet-Based Wearable Patch Sensor Design for Continuous Cardiovascular System Monitoring in Postoperative Settings.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 4;13(6):615. doi: 10.3390/bios13060615. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37366980 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of visual stethoscopes for detecting bronchospasm in a patient under general anesthesia - A case report.Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2025 Jul;20(3):277-282. doi: 10.17085/apm.24194. Epub 2025 Jul 23. Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2025. PMID: 40792372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rice M.L., Doyle D.J. Comparison of phonocardiographic monitoring locations; Proceedings of the 17th International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society; Montreal, QC, Canada. 20–23 September 1995; pp. 685–686.
-
- Shin J., Kim Y., Lim S., Cha E., Lee T. Design technology in portable digital esophageal stethoscope; Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Networked Computing; Gumi, Korea. 26–28 September 2011; pp. 94–97.
-
- Moon Y.J., Bechtel A.J., Kim S.H., Kim J.W., Thiele R.H., Blank R.S. Detection of intratracheal accumulation of thick secretions by using continuous monitoring of respiratory acoustic spectrum: A preliminary analysis. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2020;34:763–770. doi: 10.1007/s10877-019-00359-z. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

