Weak Cross-Lineage Neutralization by Anti SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antibodies after Natural Infection or Vaccination Is Rescued by Repeated Immunological Stimulation
- PMID: 34696232
- PMCID: PMC8537215
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9101124
Weak Cross-Lineage Neutralization by Anti SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antibodies after Natural Infection or Vaccination Is Rescued by Repeated Immunological Stimulation
Abstract
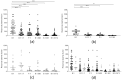
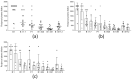
After over one year of evolution, through billions of infections in humans, SARS-CoV-2 has evolved into a score of slightly divergent lineages. A few different amino acids in the spike proteins of these lineages can hamper both natural immunity against reinfection, and vaccine efficacy. In this study, the in vitro neutralizing potency of sera from convalescent COVID-19 patients and vaccinated subjects was analyzed against six different SARS-CoV-2 lineages, including the latest B.1.617.2 (or Delta variant), in order to assess the cross-neutralization by anti-spike antibodies. After both single dose vaccination, or natural infection, the neutralizing activity was low and fully effective only against the original lineage, while a double dose or a single dose of vaccine, even one year after natural infection, boosted the cross-neutralizing activity against different lineages. Neither binding, nor the neutralizing activity of sera after vaccination, could predict vaccine failure, underlining the need for additional immunological markers. This study points at the importance of the anamnestic response and repeated vaccine stimulations to elicit a reasonable cross-lineage neutralizing antibody response.
Keywords: BAU; COVID; SARS; anamnestic response; neutralizing antibodies; vaccine; vaccine dose.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Voysey M., Clemens S.A.C., Madhi S.A., Weckx L.Y., Folegatti P.M., Aley P.K., Angus B., Baillie V.L., Barnabas S.L., Bhorat Q.E., et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 2021;397:99–111. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32661-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Solforosi L., Kuipers H., Jongeneelen M., Rosendahl Huber S.K., van der Lubbe J.E.M., Dekking L., Czapska-Casey D.N., Izquierdo Gil A., Baert M.R.M., Drijver J., et al. Immunogenicity and efficacy of one and two doses of Ad26.COV2.S COVID vaccine in adult and aged NHP. J. Exp. Med. 2021;218:e20202756. doi: 10.1084/jem.20202756. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

