ZIKV Infection and miRNA Network in Pathogenesis and Immune Response
- PMID: 34696422
- PMCID: PMC8541119
- DOI: 10.3390/v13101992
ZIKV Infection and miRNA Network in Pathogenesis and Immune Response
Abstract
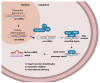
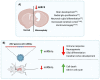
Over the years, viral infections have caused severe illness in humans. Zika Virus (ZIKV) is a flavivirus transmitted by mosquito vectors that leads to notable neurological impairment, whose most dramatic impact is the Congenital ZIKV Syndrome (CZS). ZIKV targets neuronal precursor cells leading to apoptosis and further impairment of neuronal development, causing microcephaly, lissencephaly, ventriculomegaly, and calcifications. Several regulators of biological processes are involved in CZS development, and in this context, microRNAs (miRNAs) seem to have a fundamental role. miRNAs are important regulators of protein translation, as they form the RISC silencing complex and interact with complementary mRNA target sequences to further post-transcriptional repression. In this context, little is known about their participation in the pathogenesis of viral infections. In this review, we discuss how miRNAs could relate to ZIKV and other flavivirus infections.
Keywords: ZIKV; flavivirus; microRNAs; viral infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrated MicroRNA and mRNA Profiling in Zika Virus-Infected Neurons.Viruses. 2019 Feb 16;11(2):162. doi: 10.3390/v11020162. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30781519 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide Integrative Analysis of Zika-Virus-Infected Neuronal Stem Cells Reveals Roles for MicroRNAs in Cell Cycle and Stemness.Cell Rep. 2019 Jun 18;27(12):3618-3628.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.059. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31216479 Free PMC article.
-
In silico analysis revealed Zika virus miRNAs associated with viral pathogenesis through alteration of host genes involved in immune response and neurological functions.J Med Virol. 2019 Sep;91(9):1584-1594. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25505. Epub 2019 Jun 6. J Med Virol. 2019. PMID: 31095749
-
Advances in Zika Virus⁻Host Cell Interaction: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 4;20(5):1101. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051101. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30836648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vav Proteins in Development of the Brain: A Potential Relationship to the Pathogenesis of Congenital Zika Syndrome?Viruses. 2022 Feb 14;14(2):386. doi: 10.3390/v14020386. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune Regulation in the Testis and Epididymis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1469:25-47. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-82990-1_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40301251 Review.
-
Zika Virus Infection and Antibody Neutralization in FcRn Expressing Placenta and Engineered Cell Lines.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Nov 30;10(12):2059. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10122059. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36560469 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of host miRNAs in the flavivirus 3´UTR genome: From bioinformatics predictions to practical approaches.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Oct 13;12:976843. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.976843. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36310869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory Role of Host MicroRNAs in Flaviviruses Infection.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 11;13:869441. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.869441. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35479613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNAs Control Antiviral Immune Response, Cell Death and Chemotaxis Pathways in Human Neuronal Precursor Cells (NPCs) during Zika Virus Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 7;23(18):10282. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810282. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142200 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

