Towards a Precision Medicine Approach and In Situ Vaccination against Prostate Cancer by PSMA-Retargeted oHSV
- PMID: 34696515
- PMCID: PMC8541339
- DOI: 10.3390/v13102085
Towards a Precision Medicine Approach and In Situ Vaccination against Prostate Cancer by PSMA-Retargeted oHSV
Abstract
Prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is a specific high frequency cell surface marker of prostate cancers. Theranostic approaches targeting PSMA show no major adverse effects and rule out off-tumor toxicity. A PSMA-retargeted oHSV (R-405) was generated which both infected and was cytotoxic exclusively for PSMA-positive cells, including human prostate cancer LNCaP and 22Rv1 cells, and spared PSMA-negative cells. R-405 in vivo efficacy against LLC1-PSMA and Renca-PSMA tumors consisted of inhibiting primary tumor growth, establishing long-term T immune response, immune heating of the microenvironment, de-repression of the anti-tumor immune phenotype, and sensitization to checkpoint blockade. The in situ vaccination protected from distant challenge tumors, both PSMA-positive and PSMA-negative, implying that it was addressed also to LLC1 tumor antigens. PSMA-retargeted oHSVs are a precision medicine tool worth being additionally investigated in the immunotherapeutic and in situ vaccination landscape against prostate cancers.
Keywords: PSMA; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy; in situ vaccine; oncolytic herpes simplex virus; oncolytic virus; prostate cancer; retargeting; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
GCF is a minor shareholder in Nouscom. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


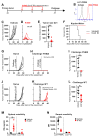


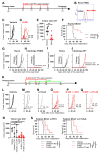
References
-
- WHO—Latest Global Cancer Data: Cancer Burden Rises to 18.1 Million New Cases and 9.6 Million Cancer Deaths in 2018. [(accessed on 12 September 2018)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/cancer/PRGlobocanFinal.pdf.
-
- The Global Cancer Observatory—All Cancers. [(accessed on 1 December 2020)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/39-All-cancers-fact-sh....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

