Transvenous coil embolization of hypoglossal canal dural arteriovenous fistula using detachable coils: A case report
- PMID: 34696553
- PMCID: PMC9260460
- DOI: 10.7461/jcen.2021.E2021.08.004
Transvenous coil embolization of hypoglossal canal dural arteriovenous fistula using detachable coils: A case report
Abstract
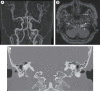
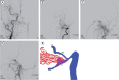
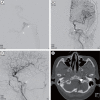
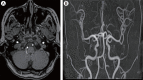
The hypoglossal canal (HC) is an unusual location of the posterior fossa dural arteriovenous fistula (AVF), which usually occurs in the transverse or sigmoid sinus. Herein, we report a case of HC dural AVF successfully treated with transvenous coil embolization using detachable coils in a 68-year-old woman who presented with headache and left pulsatile tinnitus for 2 months. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and cerebral angiography revealed left HC dural AVF. The pulsatile bruit disappeared immediately after the procedure. Follow-up MRI showed complete disappearance of the fistula. Precise localization of the fistula through careful consideration of the anatomy and transvenous coil embolization using a detachable coil can facilitate the treatment for HC dural AVF.
Keywords: Coil Embolization; Dural Arteriovenous Fistula; Hypoglossal canal.
Figures
References
-
- Choi JW, Kim BM, Kim DJ, Kim DI, Suh SH, Shin N-Y, et al. Hypoglossal canal dural arteriovenous fistula: incidence and the relationship between symptoms and drainage pattern. J Neurosurg. 2013 Oct;119(4):955–60. - PubMed
-
- Combarros O, Alvarez de Arcaya A, Berciano J. Isolated unilateral hypoglossal nerve palsy: nine cases. J Neurol. 1998 Feb;245(2):98–100. - PubMed

