A comparison of two assessment tools used in overviews of systematic reviews: ROBIS versus AMSTAR-2
- PMID: 34696810
- PMCID: PMC8543959
- DOI: 10.1186/s13643-021-01819-x
A comparison of two assessment tools used in overviews of systematic reviews: ROBIS versus AMSTAR-2
Abstract
Background: AMSTAR-2 is a 16-item assessment tool to check the quality of a systematic review and establish whether the most important elements are reported. ROBIS is another assessment tool which was designed to evaluate the level of bias present within a systematic review. Our objective was to compare, contrast and establish both inter-rater reliability and usability of both tools as part of two overviews of systematic reviews. Strictly speaking, one tool assesses methodological quality (AMSTAR-2) and the other assesses risk of bias (ROBIS), but there is considerable overlap between the tools in terms of the signalling questions.
Methods: Three reviewers independently assessed 31 systematic reviews using both tools. The inter-rater reliability of all sub-sections using each instrument (AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS) was calculated using Gwet's agreement coefficient (AC1 for unweighted analysis and AC2 for weighted analysis).
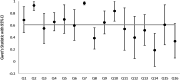
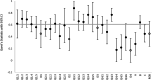
Results: Thirty-one systematic reviews were included. For AMSTAR-2, the median agreement for all questions was 0.61. Eight of the 16 AMSTAR-2 questions had substantial agreement or higher (> 0.61). For ROBIS, the median agreement for all questions was also 0.61. Eleven of the 24 ROBIS questions had substantial agreement or higher.
Conclusion: ROBIS is an effective tool for assessing risk of bias in systematic reviews and AMSTAR-2 is an effective tool at assessing quality. The median agreement between raters for both tools was identical (0.61). Reviews that included a meta-analysis were easier to rate with ROBIS; however, further developmental work could improve its use in reviews without a formal synthesis. AMSTAR-2 was more straightforward to use; however, more response options would be beneficial.
Keywords: AMSTAR-2; Methodological quality; ROBIS; Risk of bias; Systematic reviews.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Rachel Perry was an author on two of the papers under review. Philippa Davies was involved in the development of ROBIS. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quality and risk of bias appraisals of systematic reviews are inconsistent across reviewers and centers.J Clin Epidemiol. 2020 Sep;125:9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2020.04.026. Epub 2020 May 19. J Clin Epidemiol. 2020. PMID: 32416337
-
Similarities, reliability and gaps in assessing the quality of conduct of systematic reviews using AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS: systematic survey of nutrition reviews.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2021 Nov 27;21(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s12874-021-01457-w. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2021. PMID: 34837960 Free PMC article.
-
A psychometric study found AMSTAR 2 to be a valid and moderately reliable appraisal tool.J Clin Epidemiol. 2019 Oct;114:133-140. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2019.05.028. Epub 2019 May 29. J Clin Epidemiol. 2019. PMID: 31152864
-
Evaluation of the reliability, usability, and applicability of AMSTAR, AMSTAR 2, and ROBIS: protocol for a descriptive analytic study.Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 13;7(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13643-018-0746-1. Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29898777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quality Assessment and Risk of Bias of Systematic Reviews of Prophylactic Mesh for Parastomal Hernia Prevention Using AMSTAR and ROBIS Tools.World J Surg. 2019 Dec;43(12):3003-3012. doi: 10.1007/s00268-019-05139-z. World J Surg. 2019. PMID: 31440779 Review.
Cited by
-
Critical appraisal of systematic reviews of intervention studies in periodontology using AMSTAR 2 and ROBIS tools.J Clin Exp Dent. 2023 Aug 1;15(8):e678-e694. doi: 10.4317/jced.60197. eCollection 2023 Aug. J Clin Exp Dent. 2023. PMID: 37674600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical Appraisal Tools to Aid Pharmacists in Evidence-Based Practice: A Narrative Review.Can J Hosp Pharm. 2023 Mar 1;76(2):131-140. doi: 10.4212/cjhp.3281. eCollection 2023 Spring. Can J Hosp Pharm. 2023. PMID: 36998756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
User experience of applying AMSTAR 2 to appraise systematic reviews of healthcare interventions: a commentary.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2023 Mar 16;23(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12874-023-01879-8. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2023. PMID: 36927334 Free PMC article.
-
Methodological quality and reporting quality of COVID-19 living systematic review: a cross-sectional study.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2023 Jul 31;23(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s12874-023-01980-y. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2023. PMID: 37525117 Free PMC article.
-
Guidance to best tools and practices for systematic reviews1.J Pediatr Rehabil Med. 2023;16(2):241-273. doi: 10.3233/PRM-230019. J Pediatr Rehabil Med. 2023. PMID: 37302044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shea BJ, Hamel C, Wells GA, Bouter LM, Kristjansson E, Grimshaw J, Henry DA, Boers M. AMSTAR is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62:1013–1020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources