A connectome of the Drosophila central complex reveals network motifs suitable for flexible navigation and context-dependent action selection
- PMID: 34696823
- PMCID: PMC9477501
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.66039
A connectome of the Drosophila central complex reveals network motifs suitable for flexible navigation and context-dependent action selection
Abstract
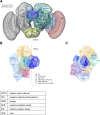
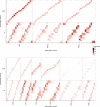
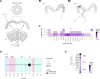
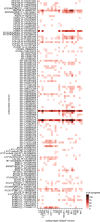
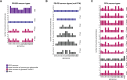
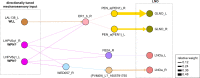
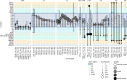
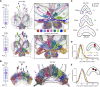
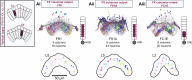
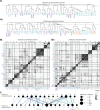
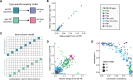
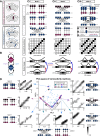
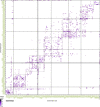
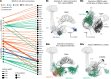
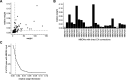
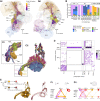
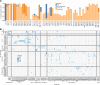
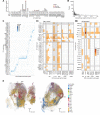
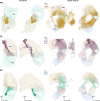
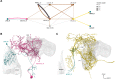
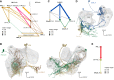
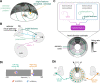
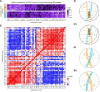
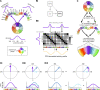
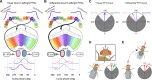
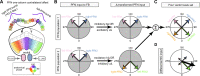
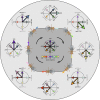
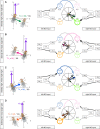
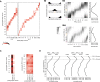
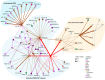
Flexible behaviors over long timescales are thought to engage recurrent neural networks in deep brain regions, which are experimentally challenging to study. In insects, recurrent circuit dynamics in a brain region called the central complex (CX) enable directed locomotion, sleep, and context- and experience-dependent spatial navigation. We describe the first complete electron microscopy-based connectome of the Drosophila CX, including all its neurons and circuits at synaptic resolution. We identified new CX neuron types, novel sensory and motor pathways, and network motifs that likely enable the CX to extract the fly's head direction, maintain it with attractor dynamics, and combine it with other sensorimotor information to perform vector-based navigational computations. We also identified numerous pathways that may facilitate the selection of CX-driven behavioral patterns by context and internal state. The CX connectome provides a comprehensive blueprint necessary for a detailed understanding of network dynamics underlying sleep, flexible navigation, and state-dependent action selection.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; central complex; connectome; insect; navigation; neuroscience; sensorimotor; sleep.
© 2021, Hulse, Haberkern, Franconville et al.
Conflict of interest statement
BH, HH, RF, DT, ST, TW, MN, MD, CD, RP, AH, GR, VJ No competing interests declared
Figures


















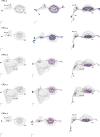
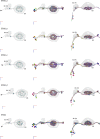
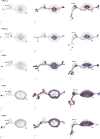
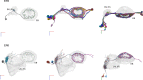















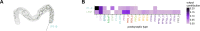








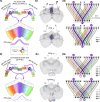
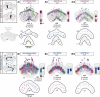
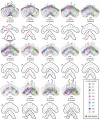
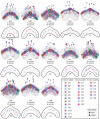













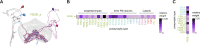










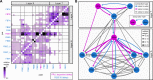



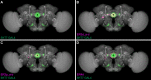
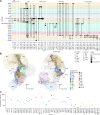
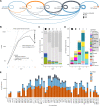







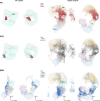

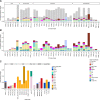

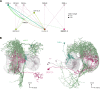
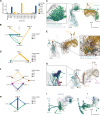





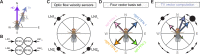







Comment in
-
Mapping the fly's 'brain in the brain'.Elife. 2021 Oct 26;10:e73963. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73963. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34696825 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiba M, Sugimoto K, Aoki R, Murakami R, Miyashita T, Hashimoto R, Hiranuma A, Yamauchi J, Ueno T, Morimoto T. Dopamine modulates the optomotor response to unreliable visual stimuli in Drosophila melanogaster. The European Journal of Neuroscience. 2020;51:822–839. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14648. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

