Mechanisms of inhibition of viral RNA replication by nucleotide analogs
- PMID: 34696838
- PMCID: PMC8474024
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.enz.2021.07.001
Mechanisms of inhibition of viral RNA replication by nucleotide analogs
Abstract
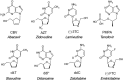
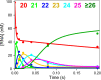
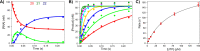
Nucleotide analogs are the cornerstone of direct acting antivirals used to control infection by RNA viruses. Here we review what is known about existing nucleotide/nucleoside analogs and the kinetics and mechanisms of RNA and DNA replication, with emphasis on the SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) in comparison to HIV reverse transcriptase and Hepatitis C RdRp. We demonstrate how accurate kinetic analysis reveals surprising results to explain the effectiveness of antiviral nucleoside analogs providing guidelines for the design of new inhibitors.
Keywords: Coronavirus; Enzyme specificity; Nucleoside analogs; Polymerase kinetics; Proofreading exonuclease; RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; Remdesivir; SARS CoV-2; Single-turnover kinetics.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



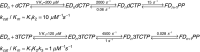


Similar articles
-
Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency.J Biol Chem. 2020 May 15;295(20):6785-6797. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013679. Epub 2020 Apr 13. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32284326 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Study on the Optimal Nucleotide Analogue Concentration and Rate Limiting Nucleotide of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 27;23(15):8302. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158302. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955442 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 polymerase stalling by remdesivir.Nat Commun. 2021 Jan 12;12(1):279. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20542-0. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33436624 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities and Challenges in Targeting the Proofreading Activity of SARS-CoV-2 Polymerase Complex.Molecules. 2022 May 3;27(9):2918. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092918. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleosides and emerging viruses: A new story.Drug Discov Today. 2022 Jul;27(7):1945-1953. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2022.02.013. Epub 2022 Feb 19. Drug Discov Today. 2022. PMID: 35189369 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Milestones in the discovery of hepatitis C.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Oct 7;28(37):5395-5402. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i37.5395. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36312838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 and the promise of small molecule therapeutics: Are there lessons to be learnt?Pharmacol Res. 2022 May;179:106201. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106201. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Pharmacol Res. 2022. PMID: 35367622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interfering with nucleotide excision by the coronavirus 3'-to-5' exoribonuclease.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 11;51(1):315-336. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1177. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36546762 Free PMC article.
-
An exonuclease-resistant chain-terminating nucleotide analogue targeting the SARS-CoV-2 replicase complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 9;52(3):1325-1340. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1194. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38096103 Free PMC article.
-
Mpox (formerly monkeypox): pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Dec 27;8(1):458. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01675-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 38148355 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gordon C.J., Tchesnokov E.P., Woolner E., Perry J.K., Feng J.Y., Porter D.P., Gotte M. Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency. J. Biol. Chem. 2020;295:6785–6797. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013679. 32284326 Epub 2020/04/15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shannon A., Selisko B., Le N.T., Huchting J., Touret F., Piorkowski G., Fattorini V., Ferron F., Decroly E., Meier C., et al. Rapid incorporation of Favipiravir by the fast and permissive viral RNA polymerase complex results in SARS-CoV-2 lethal mutagenesis. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:4682. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18463-z. 32943628 Epub 2020/09/19. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
