Effects of Wild Yam Root (Dioscorea villosa) Extract on the Gene Expression Profile of Triple-negative Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 34697066
- PMCID: PMC8569819
- DOI: 10.21873/cgp.20294
Effects of Wild Yam Root (Dioscorea villosa) Extract on the Gene Expression Profile of Triple-negative Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
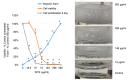
Background/aim: Wild yam extract [Dioscorea villosa, (WYE)] is consistently lethal at low IC50s across diverse cancer-lines in vitro. Unlike traditional anti-cancer botanicals, WYE contains detergent saponins which reduce oil-water interfacial tensions causing disintegration of lipid membranes and causing cell lysis, creating an interfering variable. Here, we evaluate WYE at sub-lethal concentrations in MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells.
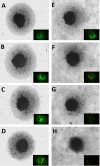
Materials and methods: Quantification of saponins, membrane potential, lytic death and sub-lethal WYE changes in whole transcriptomic (WT) mRNA, miRNAs and biological parameters were evaluated.
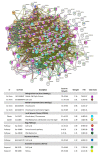
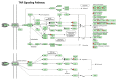
Results: WYE caused 346 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) out of 48,226 transcripts tested; where up-regulated DEGS reflect immune stimulation, TNF signaling, COX2, cytokine release and cholesterol/steroid biosynthesis. Down-regulated DEGs reflect losses in cell division cycle (CDC), cyclins (CCN), cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), centromere proteins (CENP), kinesin family members (KIFs) and polo-like kinases (PLKs), which were in alignment with biological studies.
Conclusion: Sub-lethal concentrations of WYE appear to evoke pro-inflammatory, steroid biosynthetic and cytostatic effects in TNBC cells.
Keywords: Dioscorea; Immune stimulation; breast cancer; cell cycle; wild yam.
Copyright© 2021, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures





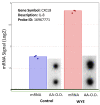
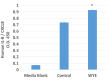
References
-
- Aumsuwan P, Khan SI, Khan IA, Avula B, Walker LA, Helferich WG, Katzenellenbogen BS, Dasmahapatra AK. Evaluation of wild yam (Dioscorea villosa) root extract as a potential epigenetic agent in breast cancer cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2015;51(1):59–71. doi: 10.1007/s11626-014-9807-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chiang CT, Way TD, Tsai SJ, Lin JK. Diosgenin, a naturally occurring steroid, suppresses fatty acid synthase expression in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells through modulating Akt, mTOR and JNK phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 2007;581(30):5735–5742. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.11.021. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
