Hemodynamic Alteration in the Liver in Acute Hepatitis: A Quantitative Evaluation Using Computed Tomographic Perfusion
- PMID: 34697192
- PMCID: PMC8627711
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.12656
Hemodynamic Alteration in the Liver in Acute Hepatitis: A Quantitative Evaluation Using Computed Tomographic Perfusion
Abstract
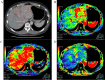
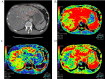
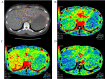
Background/aim: We aimed to elucidate the hemodynamic alterations in the liver of patients with acute hepatitis (AH) using computed tomography perfusion imaging.
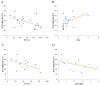
Patients and methods: For 14 patients with AH and nine patients with no disease (ND group), we compared the mean arterial blood flow (AF), portal blood flow (PF) and perfusion index (%) [PI=AF/(AF+PF) ×100] of the right and left liver lobes and investigated their relationship with clinical factors.
Results: The mean PI of the right lobe in the AH group (30.5±10.0%) was significantly higher than that in the ND group (20.8±9.7%) (p=0.031). For all patients of the AH and ND groups, the PI of the right lobe was increased as the prothrombin time decreased (R=-0.56, p=0.006) and as the prothrombin time-international normalized ratio increased (R=0.48, p=0.02).
Conclusion: The PI of the right liver lobe may increase in AH and may be a predictive parameter for the severity of hepatic failure.
Keywords: Acute hepatitis; CT perfusion; hemodynamic alteration.
Copyright © 2021 International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Akihiro Nishie was a staff member of joint research departments in Kyushu University with Canon Medical Systems Corporation. He received a research grant from Canon Medical Systems Corporation. The other Authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
