Heterotrophic bacterial diazotrophs are more abundant than their cyanobacterial counterparts in metagenomes covering most of the sunlit ocean
- PMID: 34697433
- PMCID: PMC8941151
- DOI: 10.1038/s41396-021-01135-1
Heterotrophic bacterial diazotrophs are more abundant than their cyanobacterial counterparts in metagenomes covering most of the sunlit ocean
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Heterotrophic bacterial diazotrophs are more abundant than their cyanobacterial counterparts in metagenomes covering most of the sunlit ocean.ISME J. 2022 Apr;16(4):1203. doi: 10.1038/s41396-021-01173-9. ISME J. 2022. PMID: 35058585 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
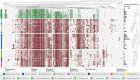
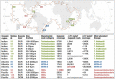
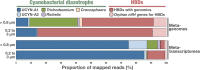
Biological nitrogen fixation contributes significantly to marine primary productivity. The current view depicts few cyanobacterial diazotrophs as the main marine nitrogen fixers. Here, we used 891 Tara Oceans metagenomes derived from surface waters of five oceans and two seas to generate a manually curated genomic database corresponding to free-living, filamentous, colony-forming, particle-attached, and symbiotic bacterial and archaeal populations. The database provides the genomic content of eight cyanobacterial diazotrophs including a newly discovered population related to known heterocystous symbionts of diatoms, as well as 40 heterotrophic bacterial diazotrophs that considerably expand the known diversity of abundant marine nitrogen fixers. These 48 populations encapsulate 92% of metagenomic signal for known nifH genes in the sunlit ocean, suggesting that the genomic characterization of the most abundant marine diazotrophs may be nearing completion. Newly identified heterotrophic bacterial diazotrophs are widespread, express their nifH genes in situ, and also occur in large planktonic size fractions where they might form aggregates that provide the low-oxygen microenvironments required for nitrogen fixation. Critically, we found heterotrophic bacterial diazotrophs to be more abundant than cyanobacterial diazotrophs in most metagenomes from the open oceans and seas, emphasizing the importance of a wide range of heterotrophic populations in the marine nitrogen balance.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to International Society for Microbial Ecology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Boyd PW. Toward quantifying the response of the oceans’ biological pump to climate change. Front Mar Sci. 2015. 10.3389/fmars.2015.00077.
-
- Charlson RJ, Lovelock JE, Andreae MO, Warren SG. Oceanic phytoplankton, atmospheric sulphur, cloud albedo and climate. Nature. 1987;326:655–61.
-
- Falkowski PG, Barber RT, Smetacek V. Biogeochemical controls and feedbacks on ocean primary production. Science (80-) 1998;281:200–6. - PubMed
-
- Arrigo KR. Marine microorganisms and global nutrient cycles. Nature. 2005;437:349–55. - PubMed
-
- Sanders R, Henson SA, Koski M, De La Rocha CL, Painter SC, Poulton AJ, et al. The biological carbon pump in the North Atlantic. Prog Oceanogr e-pub print. 2014 doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2014.05.005. - DOI

