Psychological well-being in people with multiple sclerosis: a descriptive review of the effects obtained with mindfulness interventions
- PMID: 34697659
- PMCID: PMC8724219
- DOI: 10.1007/s10072-021-05686-1
Psychological well-being in people with multiple sclerosis: a descriptive review of the effects obtained with mindfulness interventions
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Psychological well‑being in people with multiple sclerosis: a descriptive review of the effects obtained with mindfulness interventions.Neurol Sci. 2022 Mar;43(3):2167. doi: 10.1007/s10072-021-05812-z. Neurol Sci. 2022. PMID: 34913096 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
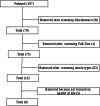
Multiple sclerosis is a neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disease causing several psychosocial problems that significantly impairs quality of life. The most common physical and mental symptoms are anxiety, depression, stress, fatigue, and pain. Several studies investigated the effectiveness of non-pharmacological approaches in improving psychological well-being. This review focused on the impact of mindfulness interventions in patients with multiple sclerosis to reduce psychopathological symptoms and improve well-being. We searched on PubMed database and screening references of included studies and review articles for additional citations. From initial 107 studies, only 8 met search criteria. Our studies showed the efficacy of mindfulness treatment with a reduction in depressive symptoms, a better quality of life (both mental and physical), and a decreased level of fatigue. Findings demonstrated that mindfulness is useful for the improvement of psychological symptoms and pain management and this improvement has also been shown to have a positive impact on the quality of life and coping and adaptation strategies. However, according to the poor available clinics evidence, on cannot conclude that mindfulness interventions are superior to other active interventions in the treatment of psychological symptoms of SM.
Keywords: Anxiety; Depression; Mindfulness; Multiple sclerosis; Pain; Psychotherapy.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Allone, C., Corallo, F., Scarlata, F., Formica, C., Cartella, E., Lo Buono, V., ... & Marino, S. (2019). Mindfulness interventions and pain management in a patient with encephalomyelitis. Complementary therapies in clinical practice, 36, 69-71. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, M., Lau, S., Shapiro, L., Carlson, N. D., Anderson, J., Carmody Segal, Z. V., . . . Devins, G. (2004). Mindfulness: a proposed opera- tional definition. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 11, 230– 241.
-
- Carletto S., Tesio V., Borghi M., Francone D., Scavelli F., Bertino G, et al. (2017), The effectiveness of a body-affective mindfulness intervention for multiple sclerosis patients with depressive symptoms: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, Article 2083. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chiesa A. The difficulty of defining mindfulness: current thought and critical. Issues Mindfulness. 2013;4(3):255–268. doi: 10.1007/s12671-012-0123-4. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous