Renal Complications and Duration of Diabetes: An International Comparison in Persons with Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 34697764
- PMCID: PMC8586278
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-021-01169-w
Renal Complications and Duration of Diabetes: An International Comparison in Persons with Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
Introduction: Renal complications are both a marker of previous suboptimal glycaemic control and a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease in persons with type 1 diabetes (T1D). The aim of the study was to evaluate the prevalence of renal complications in persons with T1D in four geographical regions.
Methods: Nationwide registry data from Austria/Germany, Sweden and the US were used to estimate the prevalence of renal complications from January 2016 until September 2018. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) and albuminuria in the study population and each registry were analysed by diabetes duration. Risk factors for renal complications were described by registry.
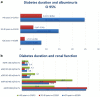
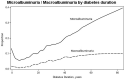
Results: In the total cohort of 78.926 adults with T1D, mean age was 44.4 ± 18.43 years and mean diabetes duration was 21.6 ± 22 years. Mean estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was 94.0 ± 31.45 ml/min, 13.0% had microalbuminuria and 3.9% had macroalbuminuria. Mean age, diabetes duration, use of insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring, as well as presence of albuminuria, varied between registries. Albuminuria was present in approximately 10% of persons with diabetes duration < 20 years and impaired renal function (eGFR < 60 ml/min) was present in 17%. In persons with diabetes duration > 40 years, approximately one-third had albuminuria and 25% had impaired renal function.
Conclusions: This analysis used three nationwide registries of persons with T1D. Despite recent use of more effective diabetes therapies, a substantial proportion of persons with T1D have renal complications at < 20 years after diagnosis. Efficient glucose-lowering and renal-protective strategies are needed in persons with T1D.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Macroalbuminuria; Microalbuminuria; Nephropathy; Renal complications; Type 1 diabetes.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
The kidney and cardiovascular outcome trials.J Diabetes. 2018 Feb;10(2):88-89. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12616. J Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 29031006
-
Prevalence and risk factors of albuminuria and chronic kidney disease in Chinese population with type 2 diabetes and impaired glucose regulation: Shanghai diabetic complications study (SHDCS).Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009 Dec;24(12):3724-31. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp349. Epub 2009 Jul 17. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009. PMID: 19617258
-
Risk of Progression of Nonalbuminuric CKD to End-Stage Kidney Disease in People With Diabetes: The CRIC (Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort) Study.Am J Kidney Dis. 2018 Nov;72(5):653-661. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.02.364. Epub 2018 May 18. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018. PMID: 29784612
-
Prevalence of albuminuria in Australia: the AusDiab Kidney Study.Kidney Int Suppl. 2004 Nov;(92):S22-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.09206.x. Kidney Int Suppl. 2004. PMID: 15485411 Review.
-
Relationships among microalbuminuria, insulin resistance and renal-cardiac complications in insulin dependent and non insulin dependent diabetes.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 1997;105 Suppl 2:1-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1211783. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 1997. PMID: 9288531 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk factors, mortality trends and cardiovasuclar diseases in people with Type 1 diabetes and controls: A Swedish observational cohort study.Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2022 Jul 22;21:100469. doi: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2022.100469. eCollection 2022 Oct. Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2022. PMID: 35898332 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of Dexcom G5 and FreeStyle Libre sensors tested simultaneously in people with type 1 or 2 diabetes and advanced chronic kidney disease.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Aug 6;10(22):7794-7807. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i22.7794. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 36158498 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chronic kidney disease in type 1 diabetes: translation of novel type 2 diabetes therapeutics to individuals with type 1 diabetes.Diabetologia. 2024 Jan;67(1):3-18. doi: 10.1007/s00125-023-06015-1. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Diabetologia. 2024. PMID: 37801140 Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Sotagliflozin in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and CKD.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2025 May 1;36(5):890-900. doi: 10.1681/ASN.0000000540. Epub 2024 Nov 1. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39485484
-
Modeling Cardiorenal Protection with Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition in Type 1 Diabetes: An Analysis of DEPICT-1 and DEPICT-2.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2025 Apr 1;20(4):529-538. doi: 10.2215/CJN.0000000641. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39918875
References
-
- nFacts F, Diabetes ON. Centers Dis Control Prev US Dep Heal Hum Serv 2011. National Diabetes Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “National diabetes fact sheet: national estimates and general information on diabetes and prediabetes in the United States”. Atlanta: US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Con, 2011.
-
- Schwandt A, Bergis D, Denkinger M, Gollisch K, Sandig D, Stingl H, Zimny S, Holl RW. Risk factors for decline in renal function among young adults with type 1 diabetes: analysis of real-life data from the German/Austrian DPV registry. J Diabetes Complicat. 2018;32(10):940–946. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2018.07.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hallström S, Pivodic A, Rosengren A, Ólafsdóttir AF, Svensson A-M, Lind M. Risk factors for atrial fibrillation in persons with type 1 diabetes, an observational cohort study of 36 258 patients from the Swedish National Diabetes Register. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(8):1530–1538. doi: 10.2337/dc18-2457. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

