Serum tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and interleukin-17 relate to anxiety and depression risks to some extent in non-small cell lung cancer survivor
- PMID: 34697903
- PMCID: PMC9060128
- DOI: 10.1111/crj.13457
Serum tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and interleukin-17 relate to anxiety and depression risks to some extent in non-small cell lung cancer survivor
Abstract
Introduction: Inflammatory cytokines are proposed as modulators for the pathogenesis of anxiety and depression (anxiety/depression), and anxiety/depression are frequently existed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) survivors. However, no published study has explored the association of inflammation cytokines with anxiety/depression in NSCLC survivors.
Objectives: We aimed to evaluate serum tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-17 (IL-17) levels, and their correlations with anxiety/depression in NSCLC survivors.
Methods: Totally, 217 NSCLC survivors and 200 controls were recruited. Then, inflammatory cytokines in serum samples were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Besides, their anxiety/depression status was assessed by Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS).
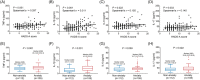
Results: HADS-anxiety score, anxiety rate, anxiety severity, HADS-depression score, depression rate, and depression severity were all increased in NSCLC survivors compared with controls (all P < 0.001). Regarding inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-17 levels were higher (all P < 0.01), while IL-6 (P = 0.105) level was of no difference in NSCLC survivors compared with controls. Furthermore, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-17 were all positively associated with HADS-A score (all P < 0.05), anxiety occurrence (all P < 0.05), HADS-D score (all P < 0.05), and depression occurrence (all P < 0.05) in NSCLC survivors, while the correlation-coefficients were weak. Additionally, multivariate logistic regression analyses disclosed that TNF-α (both P < 0.05) and IL-1β (both P < 0.001) were independently correlated with increased anxiety and depression risks in NSCLC survivors.
Conclusion: Serum TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-17 are related to increased anxiety and depression risks to some extent in NSCLC survivors.
Keywords: anxiety; depression; interleukin-1β; non-small cell lung cancer; tumor necrosis factor-α.
© 2021 The Authors. The Clinical Respiratory Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and management of non‐small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553(7689):446‐454. - PubMed
-
- Henshall C, Davey Z. Development of an app for lung cancer survivors (iEXHALE) to increase exercise activity and improve symptoms of fatigue, breathlessness and depression. Psychooncology. 2020;29(1):139‐147. - PubMed
-
- Asamura H, Goya T, Koshiishi Y, et al. A Japanese Lung Cancer Registry study: prognosis of 13,010 resected lung cancers. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3(1):46‐52. - PubMed
-
- Jankowska‐Polanska B, Polanski J, Chabowski M, Rosinczuk J, Mazur G. Influence of coping strategy on perception of anxiety and depression in patients with non‐small cell lung cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1251:57‐70. - PubMed

