Expression and Display of Glycoengineered Antibodies and Antibody Fragments with an Engineered Yeast Strain
- PMID: 34698072
- PMCID: PMC8544235
- DOI: 10.3390/antib10040038
Expression and Display of Glycoengineered Antibodies and Antibody Fragments with an Engineered Yeast Strain
Abstract
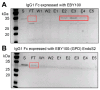
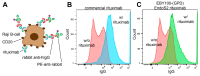
Interactions with cell surface receptors enhance the therapeutic properties of many important antibodies, including the low-affinity Fc γ Receptors (FcγRs). These interactions require proper processing of the immunoglobulin G Fc N-glycan, and eliminating the N-glycan abolishes binding, restricting antibody production to mammalian expression platforms. Yeasts, for example, generate extensively mannosylated N-glycans that are unsuitable for therapeutics. However, Fc with a specifically truncated N-glycan still engages receptors with considerable affinity. Here we describe the creation and applications of a novel Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain that specifically modifies the IgG1 Fc domain with an N-glycan consisting of a single N-acetylglucosamine residue. This strain displayed glycoengineered Fc on its surface for screening yeast surface display libraries and also served as an alternative platform to produce glycoengineered Rituximab. An IgG-specific endoglycosidase (EndoS2) truncates the IgG1 Fc N-glycan. EndoS2 was targeted to the yeast ER using the signal peptide from the yeast protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) and a yeast ER retention signal (HDEL). Furthermore, >99% of the yeast expressed Rituximab displayed the truncated glycoform as determined by SDS-PAGE and ESI-MS analyses. Lastly, the yeast expressed Rituximab engaged the FcγRIIIa with the expected affinity (KD = 2.0 ± 0.5 μM) and bound CD20 on Raji B cells.
Keywords: EndoS2; human Fc gamma receptor IIIa (FcγIIIa); human immunoglobulin 1 (hIgG1); truncated N-glycan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
CD16a with oligomannose-type N-glycans is the only "low-affinity" Fc γ receptor that binds the IgG crystallizable fragment with high affinity in vitro.J Biol Chem. 2018 Oct 26;293(43):16842-16850. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004998. Epub 2018 Sep 13. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30213862 Free PMC article.
-
Glycoengineered Monoclonal Antibodies with Homogeneous Glycan (M3, G0, G2, and A2) Using a Chemoenzymatic Approach Have Different Affinities for FcγRIIIa and Variable Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Activities.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 22;10(7):e0132848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132848. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26200113 Free PMC article.
-
Restricted processing of CD16a/Fc γ receptor IIIa N-glycans from primary human NK cells impacts structure and function.J Biol Chem. 2018 Mar 9;293(10):3477-3489. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001207. Epub 2018 Jan 12. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29330305 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody glycosylation and its impact on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of monoclonal antibodies and Fc-fusion proteins.J Pharm Sci. 2015 Jun;104(6):1866-1884. doi: 10.1002/jps.24444. Epub 2015 Apr 14. J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 25872915 Review.
-
New anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of B-cell lymphoid malignancies.BioDrugs. 2011 Feb 1;25(1):13-25. doi: 10.2165/11539590-000000000-00000. BioDrugs. 2011. PMID: 21090841 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae for medical applications.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 Jan 9;24(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02625-5. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 39789534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
One N-glycan regulates natural killer cell antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and modulates Fc γ receptor IIIa / CD16a structure.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 25:2024.06.17.599285. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.17.599285. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Oct 25;13:RP100083. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100083. PMID: 38948809 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
One N-glycan regulates natural killer cell antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and modulates Fc γ receptor IIIa/CD16a structure.Elife. 2024 Oct 25;13:RP100083. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100083. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39453384 Free PMC article.
-
Humanization of Yeasts for Glycan-Type End-Products.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jul 7;13:930658. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.930658. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35875538 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Duehr J., Wohlbold T.J., Oestereich L., Chromikova V., Amanat F., Rajendran M., Gomez-Medina S., Mena I., Tenoever B.R., García-Sastre A., et al. Novel Cross-Reactive Monoclonal Antibodies against Ebolavirus Glycoproteins Show Protection in a Murine Challenge Model vaccines and antiviral agents Crossm. J. Virol. 2017;91:652–669. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00652-17. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khoury D.S., Cromer D., Reynaldi A., Schlub T.E., Wheatley A.K., Juno J.A., Subbarao K., Kent S.J., Triccas J.A., Davenport M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021;27:1205–1211. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01377-8. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

