Testosterone Therapy With Subcutaneous Injections: A Safe, Practical, and Reasonable Option
- PMID: 34698352
- PMCID: PMC9006970
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgab772
Testosterone Therapy With Subcutaneous Injections: A Safe, Practical, and Reasonable Option
Abstract
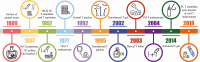
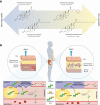
Context: Injections with intramuscular (IM) testosterone esters have been available for almost 8 decades and not only result in predictable serum testosterone levels but are also the most inexpensive modality. However, they are difficult to self-administer and associated with some discomfort. Recently, subcutaneous (SC) administration of testosterone esters has gained popularity, as self-administration is easier with this route. Available data, though limited, support the feasibility of this route. Here we review the pharmacokinetics and safety of SC testosterone therapy with both long- and ultralong-acting testosterone esters. In addition, we provide guidance for clinicians on how to counsel and manage their patients who opt for the SC route.
Evidence acquisition: Systematic review of available literature on SC testosterone administration including clinical trials, case series, and case reports. We also review the pharmacology of testosterone absorption after SC administration.
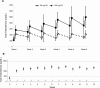
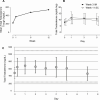
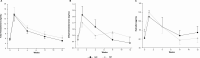
Evidence synthesis: Available evidence, though limited, suggests that SC testosterone therapy in doses similar to those given via IM route results in comparable pharmacokinetics and mean serum testosterone levels. With appropriate training, patients should be able to safely self-administer testosterone esters SC with relative ease and less discomfort compared with the IM route.
Conclusion: Although studies directly comparing the safety of SC vs IM administration of testosterone esters are desirable, clinicians should consider discussing the SC route with their patients because it is easier to self-administer and has the potential to improve patient adherence.
Keywords: androgen deficiency; androgens; hypogonadism; testosterone replacement therapy; transgender.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

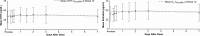
References
-
- Bhasin S, Brito JP, Cunningham GR, et al. Testosterone therapy in men with hypogonadism: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(5):1715-1744. - PubMed
-
- Hembree WC, Cohen-Kettenis PT, Gooren L, et al. Endocrine treatment of gender-dysphoric/gender-incongruent persons: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(11):3869-3903. - PubMed
-
- Brown-Séquard CE. Note on the effects produced on man by subcutaneous injections of a liquid obtained from the testicles of animals. Lancet. 1889;134(3438):105-107.
-
- David K, Dingemanse E, Freud J, Laqueur E. Über krystallinisches männliches Hormon aus Hoden (Testosteron), wirksamer als aus Harn oder aus Cholesterin bereitetes Androsteron. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1935;233(5-6):281-283.
-
- Butenandt A, Hanisch G. Über Testosteron. Umwandlung des Dehydro-androsterons in Androstendiol und Testosteron; ein Weg zur Darstellung des Testosterons aus Cholesterin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1935;237(1-3):89-97.

