Factors for the Primary Prevention of Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies
- PMID: 34698654
- PMCID: PMC8957681
- DOI: 10.34172/jrhs.2021.57
Factors for the Primary Prevention of Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies
Abstract
Background: This report provided the effect of 15 preventable factors on the risk of breast cancer incidence.
Study design: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods: A detailed research was conducted on PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus databases in January 2020. Reference lists were also screened. Prospective cohort studies addressing the associations between breast cancer and 15 factors were analyzed. Between-study heterogeneity was investigated using the χ2, τ2, and I2 statistics. The probability of publication bias was explored using the Begg and Egger tests and trim-and-fill analysis. Effect sizes were expressed as risk ratios (RRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) using a random-effects model.
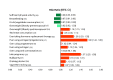
Results: Based on the results, out of 147,083 identified studies, 197 were eligible, including 19,413,702 participants. The RRs (95% CI) of factors associated with breast cancer were as follows: cigarette smoking 1.07 (1.05, 1.09); alcohol drinking 1.10 (1.07, 1.12); sufficient physical activity 0.90 (0.86, 0.95); overweight/obesity in premenopausal 0.92 (0.82, 1.03) and postmenopausal 1.18 (1.13, 1.24); nulliparity 1.16 (1.03, 1.31); late pregnancy 1.37 (1.25, 1.50); breastfeeding 0.87 (0.81, 0.93); ever using oral contraceptive 1.00 (0.96, 1.05); ever using estrogen 1.13 (1.04, 1.23); ever using progesterone 1.02 (0.84, 1.24); ever using estrogen/progesterone 1.60 (1.42, 1.80); ever taking hormone replacement therapy 1.26 (1.20, 1.32); red meat consumption 1.05 (1.00, 1.11); fruit/vegetable consumption 0.87 (0.83, 0.90); and history of radiation therapy, based on single study 1.31 (0.87, 1.98).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis provided a clear picture of several factors associated with the development of breast cancer. Moreover, the useful information in this study may be utilized for ranking and prioritizing preventable risk factors to implement effective prevention programs.
Keywords: Behavior; Breast neoplasms; Meta-analysis; Nutrition; Risk factors.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Breast cancer. Geneva: WHO; 2020 [cited 15 Feb 2020]; Available from: https://www.who.int/cancer/prevention/diagnosis-screening/breast-cancer/en/.
-
- DeSantis CE, Ma J, Gaudet MM, Newman LA, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A. et al. Breast cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:438–51. - PubMed
-
- Sifri R, Gangadharappa S, Acheson LS. Identifying and testing for hereditary susceptibility to common cancers. CA Cancer J Clin. 2004;54:309–26. - PubMed
-
- Poorolajal J, Nafissi N, Akbari ME, Mahjub H, Esmailnasab N, Babaee E. Breast cancer survival analysis based on immunohistochemistry subtypes (ER/PR/HER2): a retrospective cohort study. Arch Intern Med. 2016;19:680–6. - PubMed
-
- DeSantis CE, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, Jemal A, Siegel RL. Cancer statistics for African Americans, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:211–33. - PubMed