Tipping the balance: intricate roles of the complement system in disease and therapy
- PMID: 34698894
- PMCID: PMC8547127
- DOI: 10.1007/s00281-021-00892-7
Tipping the balance: intricate roles of the complement system in disease and therapy
Abstract
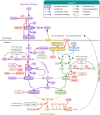
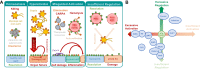
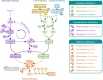
The ability of the complement system to rapidly and broadly react to microbial intruders, apoptotic cells and other threats by inducing forceful elimination responses is indispensable for its role as host defense and surveillance system. However, the danger sensing versatility of complement may come at a steep price for patients suffering from various immune, inflammatory, age-related, or biomaterial-induced conditions. Misguided recognition of cell debris or transplants, excessive activation by microbial or damaged host cells, autoimmune events, and dysregulation of the complement response may all induce effector functions that damage rather than protect host tissue. Although complement has long been associated with disease, the prevalence, impact and complexity of complement's involvement in pathological processes is only now becoming fully recognized. While complement rarely constitutes the sole driver of disease, it acts as initiator, contributor, and/or exacerbator in numerous disorders. Identifying the factors that tip complement's balance from protective to damaging effects in a particular disease continues to prove challenging. Fortunately, however, molecular insight into complement functions, improved disease models, and growing clinical experience has led to a greatly improved understanding of complement's pathological side. The identification of novel complement-mediated indications and the clinical availability of the first therapeutic complement inhibitors has also sparked a renewed interest in developing complement-targeted drugs, which meanwhile led to new approvals and promising candidates in late-stage evaluation. More than a century after its description, complement now has truly reached the clinic and the recent developments hold great promise for diagnosis and therapy alike.
Keywords: Autoimmune disease; Complement; Complement therapeutics; Hemolysis; Inflammation.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
DR and RBP are co-inventors of patents or patent applications describing therapeutic complement modulators, some of which have been licensed to Amyndas Pharmaceuticals and Gemini Therapeutics. DR has received compensation for invited lectures and/or advisory services from Roche, Novartis, Alexion, Sobi, and Greenovation.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

