A novel augmented reality-based surgical guidance system for total knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 34698930
- PMCID: PMC8595230
- DOI: 10.1007/s00402-021-04204-4
A novel augmented reality-based surgical guidance system for total knee arthroplasty
Abstract
Introduction: Many of the functional complications that arise after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) are caused by a non-optimal balance of the knee after surgery. Over the past 20 years, technology has been used in the Operating Room (OR) to help improve precision and balance. The results of Computer-Assisted Surgery (CAS) and robotic systems show improved accuracy regarding implant positioning but a relatively small improvement in patient-reported outcomes and implant survival compared to conventional TKA. Recently, Augmented Reality (AR) has been proposed as a technology that could improve accuracy in orthopaedic surgery, providing a more efficient and cost-effective solution.
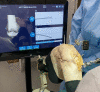
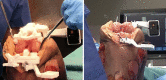
Materials and methods: This article describes a novel AR-based surgical guidance system that measures intra-operatively the effect of prosthesis alignment and positioning on soft tissue balance. The system is integrated in a pair of smart glasses and two small sensors and displays surgical targets directly in the field of view of the surgeon.
Results: The system has been used in a limited number of cases. While the preliminary experience has been positive, clinical research is ongoing to confirm to confirm the performance of the system and the impact on clinical outcomes.
Conclusion: Augmented Reality can be a valuable tool to improve accuracy in TKA. The use of smart glasses and integrated sensors improves the efficiency of the procedure, particularly when coupled with single-use instrumentation. A novel protocol for soft tissue assessment allows for a 3-dimensional evaluation of the ligaments and a better measurement of the effect of tibial rotation.
Keywords: Accuracy; Augmented reality; Balance; Computer-assisted surgery; Ligaments; TKA.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
P.P.K. and S.F.F. receive advisory fees from Medacta as part of their consultancy work.
Figures



References
-
- Evans JT, Walker RW, Evans JP, Blom AW, Sayers A, Whitehouse MR. How long does a knee replacement last? A systematic review and meta-analysis of case series and national registry reports with more than 15 years of follow-up. The Lancet. 2019;393(10172):655–663. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32531-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

