Predicting miRNA-disease associations using improved random walk with restart and integrating multiple similarities
- PMID: 34702958
- PMCID: PMC8548500
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-00677-w
Predicting miRNA-disease associations using improved random walk with restart and integrating multiple similarities
Abstract
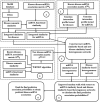
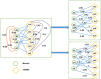
Predicting beneficial and valuable miRNA-disease associations (MDAs) by doing biological laboratory experiments is costly and time-consuming. Proposing a forceful and meaningful computational method for predicting MDAs is essential and captivated many computer scientists in recent years. In this paper, we proposed a new computational method to predict miRNA-disease associations using improved random walk with restart and integrating multiple similarities (RWRMMDA). We used a WKNKN algorithm as a pre-processing step to solve the problem of sparsity and incompletion of data to reduce the negative impact of a large number of missing associations. Two heterogeneous networks in disease and miRNA spaces were built by integrating multiple similarity networks, respectively, and different walk probabilities could be designated to each linked neighbor node of the disease or miRNA node in line with its degree in respective networks. Finally, an improve extended random walk with restart algorithm based on miRNA similarity-based and disease similarity-based heterogeneous networks was used to calculate miRNA-disease association prediction probabilities. The experiments showed that our proposed method achieved a momentous performance with Global LOOCV AUC (Area Under Roc Curve) and AUPR (Area Under Precision-Recall Curve) values of 0.9882 and 0.9066, respectively. And the best AUC and AUPR values under fivefold cross-validation of 0.9855 and 0.8642 which are proven by statistical tests, respectively. In comparison with other previous related methods, it outperformed than NTSHMDA, PMFMDA, IMCMDA and MCLPMDA methods in both AUC and AUPR values. In case studies of Breast Neoplasms, Carcinoma Hepatocellular and Stomach Neoplasms diseases, it inferred 1, 12 and 7 new associations out of top 40 predicted associated miRNAs for each disease, respectively. All of these new inferred associations have been confirmed in different databases or literatures.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Inferring miRNA-disease associations using collaborative filtering and resource allocation on a tripartite graph.BMC Med Genomics. 2021 Nov 17;14(Suppl 3):225. doi: 10.1186/s12920-021-01078-8. BMC Med Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34789252 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of MicroRNA-Disease Potential Association Based on Sparse Learning and Multilayer Random Walks.J Comput Biol. 2024 Mar;31(3):241-256. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2023.0266. Epub 2024 Feb 19. J Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 38377572
-
A novel miRNA-disease association prediction model using dual random walk with restart and space projection federated method.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 17;16(6):e0252971. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252971. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34138933 Free PMC article.
-
PBMDA: A novel and effective path-based computational model for miRNA-disease association prediction.PLoS Comput Biol. 2017 Mar 24;13(3):e1005455. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005455. eCollection 2017 Mar. PLoS Comput Biol. 2017. PMID: 28339468 Free PMC article.
-
Review of MiRNA-Disease Association Prediction.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020;21(11):1044-1053. doi: 10.2174/1389203721666200210102751. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020. PMID: 32039677 Review.
Cited by
-
Inferring pseudogene-MiRNA associations based on an ensemble learning framework with similarity kernel fusion.Sci Rep. 2023 May 31;13(1):8833. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36054-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37258695 Free PMC article.
-
A Deep Differential Analysis in Four Subtypes of Breast Cancer Based on Regulations of miRNA-mRNA.IET Syst Biol. 2025 Jan-Dec;19(1):e70020. doi: 10.1049/syb2.70020. IET Syst Biol. 2025. PMID: 40498676 Free PMC article.
-
iCluF: an unsupervised iterative cluster-fusion method for patient stratification using multiomics data.Bioinform Adv. 2024 Jan 30;4(1):vbae015. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbae015. eCollection 2024. Bioinform Adv. 2024. PMID: 38698887 Free PMC article.
-
A Survey on Computational Methods for Investigation on ncRNA-Disease Association through the Mode of Action Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 29;23(19):11498. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911498. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of methods for characterization and visualization of a protein-protein interaction network in a multi-omics integration context.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Sep 8;9:962799. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.962799. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36158572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

