COVID-19 and Health Sector Development Plans in Africa: The Impact on Maternal and Child Health Outcomes in Uganda
- PMID: 34703344
- PMCID: PMC8541793
- DOI: 10.2147/RMHP.S328004
COVID-19 and Health Sector Development Plans in Africa: The Impact on Maternal and Child Health Outcomes in Uganda
Abstract
Introduction: Health Sector Development Plans (HSDPs) aim to accelerate movement towards achieving sustainable development goals for health, reducing inequalities, and ending poverty. Reproductive, maternal, newborn and child health (RMNCH) services are vulnerable to economic imbalances, including health insecurity, unmet need for healthcare, and low health expenditure. The same vulnerability influences the potential of a country to combat global outbreaks such as the COVID-19. We aimed to provide some important insights into the impacts of COVID-19 on RMNCH indicators and outcomes of the HSDP in Uganda.
Methods: We conducted a descriptive study of secondary data obtained from the Ugandan government-led portals, supplemented by analyses of relevant articles published up to 06 May 2021 and deposited in PubMed.
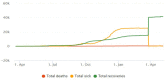
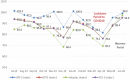
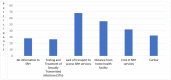
Results: Through synthesizing actionable and relevant evidence, we realized that RMNCH in Uganda is highly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic and the lockdown measures. The impact was across immunization, antenatal, sexual and reproductive health, emergency and obstetric, and postnatal care services. There was a decline sharply by 9.6% for under-five vitamin A coverage, 9% for DPT3HibHeb3 coverage, 6.8% for measles vaccination coverage, 6% for isoniazid preventive therapy coverage, and 3% for facility-based deliveries. Maternal and under-five deaths increased by 7.6% and 4%, respectively. Outreaches were rarely conducted in the lockdown period.
Conclusion: The COVID-19 pandemic has created a multitude of questions regarding the optimal policies to mitigate the disease while minimizing the unintended detrimental consequences of RMNCH. The lockdown restrictions threatened to reverse the progress made on the national HSDP for RMNCH. In Uganda, where young women are vulnerable to early marriage, unintended pregnancies, and unsafe abortion, access to RMNCH services should continue regardless of the COVID-19 status in the country. We urge that Uganda and other African countries should build resilient and sustainable health systems that can withstand emerging diseases like the COVID-19.
Keywords: Africa; COVID-19; Health Sector Development Plan; Uganda; maternal; newborn and child health; reproductive.
© 2021 Atim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources