Characteristics of COVID-19 patients up to 6 months of age admitted to a paediatric emergency department
- PMID: 34704279
- PMCID: PMC8653029
- DOI: 10.1111/apa.16166
Characteristics of COVID-19 patients up to 6 months of age admitted to a paediatric emergency department
Abstract
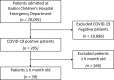
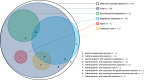
Very young age could be a potential risk factor for community-acquired severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, due to immature immune systems. We retrospectively enrolled 39 infants up to 6 months of age who had presented to our tertiary Italian children's hospital emergency room between 9 March 2020 and 8 March 2021 and tested positive for the virus. Of those, 38 had a non-specific mild or asymptomatic clinical course and only one patient was admitted to intensive care with severe symptoms. We concluded that very young infants with COVID-19 had a generally favourable disease course.
Keywords: asymptomatic; disease course; emergency room; infants; pandemic.
© 2021 Foundation Acta Paediatrica. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID‐19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323(13):1239‐1242. - PubMed
-
- Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, et al. Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19): a review. JAMA. 2020;324(8):782‐793. - PubMed
-
- Brisca G, Mariani M, Andrea Rotulo G, et al. Clinical course of COVID‐19 in children with pre‐existing medical conditions. Acta Paediatr. 2021;110(4):1291‐1292. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

