Inflammatory phenotype modulation in the respiratory tract and systemic circulation of e-cigarette users: a pilot study
- PMID: 34704852
- PMCID: PMC8715026
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00363.2021
Inflammatory phenotype modulation in the respiratory tract and systemic circulation of e-cigarette users: a pilot study
Abstract
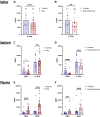
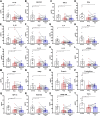
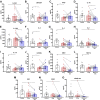
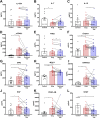
Over 40 million people use e-cigarettes worldwide, but the impact of chronic e-cigarette use on health has not been adequately defined. In particular, effects of e-cigarette aerosol inhalation on inflammation and host defenses across the body are not fully understood. We conducted a longitudinal cohort pilot study to explore changes in the inflammatory state and monocyte function of e-cigarette users (n = 20) versus healthy controls (n = 13) and to evaluate effects of e-cigarette use reduction on the same. Saliva, sputum, and blood were obtained from e-cigarette users at baseline and after a 2-wk intervention of decreased e-cigarette use. Overall, across 38 proteins quantified by multiplex, airway samples from e-cigarette users tended to have decreased levels of immunomodulatory proteins relative to healthy controls, whereas levels of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors in the circulation tended to be elevated. Specifically, e-cigarette users had lower levels of IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) in saliva (P < 0.0001), with higher IL-1Ra and growth-regulated oncogene (GRO) levels in sputum (P < 0.01 and P < 0.05, respectively), and higher levels of both TNFβ (P < 0.0001) and VEGF (P < 0.0001) in plasma. Circulating monocytes from e-cigarette users had alterations in their inflammatory phenotype in response to reduced e-cigarette use, with blunted IL-8 and IL-6 release upon challenge with bacterial lipopolysaccharide (P < 0.001 and P < 0.05, respectively), suggesting a decreased ability to appropriately respond to bacterial infection. Based on these findings, chronic inhalation of e-cigarette aerosols alters the inflammatory state of the airways and systemic circulation, raising concern for the development of both inflammatory and infectious diseases in chronic users of e-cigarettes.
Keywords: cytokine; e-cigarette; host defense; inflammation; monocyte.
Conflict of interest statement
P.A. has received research funding from AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, and Regeneron and has received consultancy fees from AstraZeneca and GlaxoSmithKline. None of the other authors has any conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Martinez U, Martinez-Loredo V, Simmons VN, Meltzer LR, Drobes DJ, Brandon KO, Palmer AM, Eissenberg T, Bullen CR, Harrell PT, Brandon TH. How does smoking and nicotine dependence change after onset of vaping? A retrospective analysis of dual users. Nicotine Tob Res 22: 764–770, 2020. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntz043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

