ACE-inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blockers (ACE-I/ARBs) therapy in COVID-19 infected dialysis patients
- PMID: 34704916
- PMCID: PMC8555537
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2021.1994419
ACE-inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blockers (ACE-I/ARBs) therapy in COVID-19 infected dialysis patients
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s). Drs. Rao and Soliman are members of the editorial board of Renal Failure.
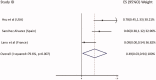
Figures
Comment on
-
Inhibitors of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 18;382(25):2462-2464. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2012924. Epub 2020 May 1. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32356625 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
COVID-19 Among US Dialysis Patients: Risk Factors and Outcomes From a National Dialysis Provider.Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 May;77(5):748-756.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.01.003. Epub 2021 Jan 17. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 33465417 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous