Brain injury after cardiac arrest: pathophysiology, treatment, and prognosis
- PMID: 34705079
- PMCID: PMC8548866
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-021-06548-2
Brain injury after cardiac arrest: pathophysiology, treatment, and prognosis
Abstract
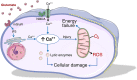
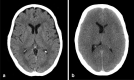
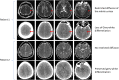
Post-cardiac arrest brain injury (PCABI) is caused by initial ischaemia and subsequent reperfusion of the brain following resuscitation. In those who are admitted to intensive care unit after cardiac arrest, PCABI manifests as coma, and is the main cause of mortality and long-term disability. This review describes the mechanisms of PCABI, its treatment options, its outcomes, and the suggested strategies for outcome prediction.
Keywords: Brain; Cardiac arrest; Coma; EEG; Hypoxia-Ischemia; Prognostication.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
CS is member of the Editorial Board of Intensive Care Medicine and co-author of studies included in the review. TC is co-author of studies included in the review. MS is a co-author of studies included in the review. He is funded by the Michael Smith Foundation of Health Research Health Professional Investigator Award, Vancouver Coastal Health Research Institute’s Clinician Scientist Award and the Canadian Institute of Health Research (grant #437644).
Figures






References
-
- Lemiale V, Dumas F, Mongardon N, Giovanetti O, Charpentier J, Chiche JD, Carli P, Mira JP, Nolan J, Cariou A. Intensive care unit mortality after cardiac arrest: the relative contribution of shock and brain injury in a large cohort. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39:1972–1980. - PubMed
-
- Geocadin RG, Callaway CW, Fink EL, Golan E, Greer DM, Ko NU, Lang E, Licht DJ, Marino BS, McNair ND, Peberdy MA, Perman SM, Sims DB, Soar J, Sandroni C, American Heart Association Emergency Cardiovascular Care C Standards for studies of neurological prognostication in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;140:e517–e542. - PubMed
-
- Buunk G, van der Hoeven JG, Meinders AE. Cerebral blood flow after cardiac arrest. Neth J Med. 2000;57:106–112. - PubMed
-
- Rossen R, Kabat H, Anderson JP. Acute arrest of cerebral circulation in man. Arch Neurol Psychiatr. 1943;50:510–528.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

