Pandemic tele-smart: a contactless tele-health system for efficient monitoring of remotely located COVID-19 quarantine wards in India using near-field communication and natural language processing system
- PMID: 34705163
- PMCID: PMC8548353
- DOI: 10.1007/s11517-021-02456-1
Pandemic tele-smart: a contactless tele-health system for efficient monitoring of remotely located COVID-19 quarantine wards in India using near-field communication and natural language processing system
Abstract
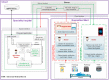
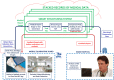
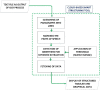
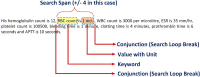
Efficient remote monitoring of the patient infected with coronavirus without spread to healthcare workers is the need of the hour. An effectual and faster communication system must be established wherein the healthcare workers at the remote quarantine ward can communicate with healthcare professionals present in specialty hospitals. Incidentally, there is a need to establish a contactless smart cloud-based connection between a specialty hospital and quarantine wards during pandemic situation. This paper proposes an initial contactless web-based tele-health clinical decision support system that integrates near-field communication (NFC) tags and a smart cloud-based structuring tool that enables the quick diagnosis of patients with COVID-19 symptoms and monitors the remotely located quarantine wards during the recent pandemic. The proposed framework consists of three-stages: (i) contactless health parameter extraction from the patient using an NFC tag; (ii) converting medical report into digital text using optical character recognition algorithm and extracting values of relevant medical-parameters using natural language processing; and (iii) smart visualization of key medical parameters. The accuracy of the proposed system from NFC reader until analysis using a novel structuring algorithm deployed in the cloud is more than 94%. Several capabilities of the proposed web-based system were compared with similar systems and tested in an authentic mock clinical setup, and the physicians found that the system is reliable and user friendly.
Keywords: Clinical decision support systems; Electronic medical records; Mobile health; Remote consultation; Telemedicine.
© 2021. International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- World Health Organisation, Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/ Accessed 15 June 2021
-
- Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) (2020) How COVID-19 spreads. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/how-COVID.... Accessed 15 June 2021
-
- World Health Organisation, Statement on the second meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee regarding the outbreak of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-...). Accessed 15 June 2021
-
- World Health Organisation (WHO) Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19, https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re.... Accessed 15 June 2021
-
- World Health Organisation, T3: Test. Treat. Track (2012) Scaling up diagnostic testing, treatment, and surveillance for malaria, https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/test_treat_track_brochure...., April 2012 (accessed 15 June 2021)
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

