Cardiovascular and renal effects of novel nonpeptide nociceptin opioid peptide receptor agonists
- PMID: 34705263
- PMCID: PMC8716424
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.15717
Cardiovascular and renal effects of novel nonpeptide nociceptin opioid peptide receptor agonists
Abstract
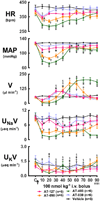
Background and purpose: Partial agonists of the nociceptin opioid peptide (NOP) receptor have potential therapeutic use as antihypertensive and water diuretics (aquaretics). To date, peptide NOP receptor ligands have failed to progress in clinical trials due to poor pharmacokinetics and adverse effects. Nonpeptide, small-molecule NOP receptor ligands may be more suitable as therapeutic agents. This study investigated the cardiovascular and renal responses produced by the novel nonpeptide NOP agonists AT-403, AT-090, AT-127, and AT-039.
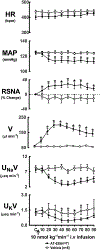
Experimental approach: Changes in mean arterial pressure (MAP), heart rate (HR), renal excretory function and occurrence of sedation and hyperphagia were determined before and after i.v. bolus injection or infusion of the NOP agonists in conscious Sprague-Dawley rats. Additional studies involving (i) measurement of renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA) and (ii) renal denervation were conducted to investigate the role of the renal nerves in the cardiorenal responses to AT-039.
Key results: Bolus i.v. injection of AT-403, AT-090, AT-127 and AT-039 produced significant decreases in MAP and HR and a sodium-sparing diuresis. AT-403, AT-090, and AT-127, but not AT-039, induced sedation and hyperphagia at all doses tested. Infusion i.v. of AT-039 produced hypotension and aquaresis without adverse central nervous system effects or change in HR, responses that were also observed in renal denervated rats.
Conclusions and implications: Nonpeptide NOP agonists decrease blood pressure and produce aquaresis in conscious rodents. Due to lack of sedation and hyperphagia, AT-039 represents a novel NOP agonist that may be useful for treatment of hypertension and/or volume overload/hyponatraemic states.
© 2021 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Alexander SP, Christopoulos A, Davenport AP, Kelly E, Mathie A, Peters JA, Veale EL, Armstrong JF, Faccenda E, Harding SD, et al. , (2021) THE CONCISE GUIDE TO PHARMACOLOGY 2021/22: G protein-coupled receptors. British Journal of Pharmacology, 178, Suppl 1:S27–S156. doi: 10.1111/bph.15538. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Asth L, Ruzza C, Malfacini D, Medeiros I, Guerrini R, Zaveri NT, Gavioli EC & Calo' G (2016) Beta-arrestin 2 rather than G protein efficacy determines the anxiolytic-versus antidepressant-like effects of nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor ligands. Neuropharmacology, 105, 434–442. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Curtis MJ, Alexander S, Cirino G, Docherty JR, George CH, Giembycz MA, Hoyer D, Insel PA, Izzo AA, MacEwan DJ, Sobey CG, Stanford SC, Teixeira MM, Wonnacot S, & Ahluwalia A (2018). Experimental design and analysis and their reporting II: updated and simplified guidance for authors and peer reviewers. British Journal of Pharmacology, 175(7), 987–993. - PMC - PubMed
-
- DiBona GF, & Sawin LL (1983). Renal nerves in renal adaptation to dietary sodium restriction. American Journal of Physiology, 245(3), F322–F328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

