Improved Biocompatibility of Intra-Arterial Poly-L-Lactic Acid Stent by Tantalum Ion Implantation : 3-Month Results in a Swine Model
- PMID: 34706407
- PMCID: PMC8590919
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2021.0009
Improved Biocompatibility of Intra-Arterial Poly-L-Lactic Acid Stent by Tantalum Ion Implantation : 3-Month Results in a Swine Model
Abstract
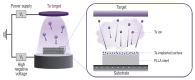
Objective: Biodegradable poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) with a highly biocompatible surface via tantalum (Ta) ion implantation can be an innovative solution for the problems associated with current biodegradable stents. The purpose of this study is to develop a Ta-implanted PLLA stent for clinical use and to investigate its biological performance capabilities.
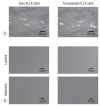
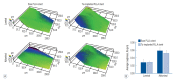
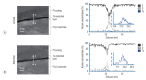
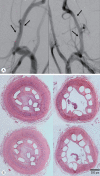
Methods: A series of in vitro and in vivo tests were used to assess the biological performance of bare and Ta-implanted PLLA stents. The re-endothelialization ability and thrombogenicity were examined through in vitro endothelial cell and platelet adhesion tests. An in vivo swine model was used to evaluate the effects of Ta ion implantation on subacute restenosis and thrombosis. Angiographic and histologic evaluations were conducted at one, two and three months post-treatment.
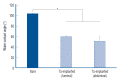
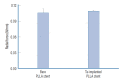
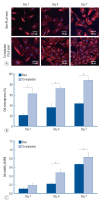
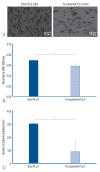
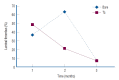
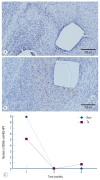
Results: The Ta-implanted PLLA stent was successfully fabricated, exhibiting a smooth surface morphology and modified layer integration. After Ta ion implantation, the surface properties were more favorable for rapid endothelialization and for less platelet attachment compared to the bare PLLA stent. In an in vivo animal test, follow-up angiography showed no evidence of in-stent stenosis in either group. In a microscopic histologic examination, luminal thrombus formation was significantly suppressed in the Ta-implanted PLLA stent group according to the 2-month follow-up assessment (21.2% vs. 63.9%, p=0.005). Cells positive for CD 68, a marker for the monocyte lineage, were less frequently identified around the Ta-implanted PLLA stent in the 1-month follow-up assessments.
Conclusion: The use of a Ta-implanted PLLA stent appears to promote re-endothelialization and anti-thrombogenicity.
Keywords: Absorbable implants; Lactic acid; Pig; Stents; Tantalum.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Barbarash LS, Bolbasov EN, Antonova LV, Matveeva VG, Velikanova EA, Shesterikov EV, et al. Surface modification of poly-ε-caprolactone electrospun fibrous scaffolds using plasma discharge with sputter deposition of a titanium target. Materials Letters. 2016;171:87–90.
-
- Bledzki AK, Jaszkiewicz A, Scherzer D. Mechanical properties of PLA composites with man-made cellulose and abaca fibres. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf. 2009;40:404–412.
-
- Chen JY, Leng YX, Tian XB, Wang LP, Huang N, Chu PK, et al. Antithrombogenic investigation of surface energy and optical bandgap and hemocompatibility mechanism of Ti(Ta+5)O2 thin films. Biomaterials. 2002;23:2545–2552. - PubMed
-
- Collet C, Asano T, Miyazaki Y, Tenekecioglu E, Katagiri Y, Sotomi Y, et al. Late thrombotic events after bioresorbable scaffold implantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Eur Heart J. 2017;38:2559–2566. - PubMed
-
- Hanawa T. Metal ion release from metal implants. Mat Sci Eng C-Bio S. 2004;24:745–752.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

